Many people often ignore their tooth loss because they think it will not have any serious consequences later. In fact, tooth loss is the leading cause of jawbone loss and will have serious consequences if not treated promptly. And with modern technology, dental implants are considered the only solution that can effectively and safely prevent the risk of jawbone loss due to tooth loss.
1. What is jawbone loss?
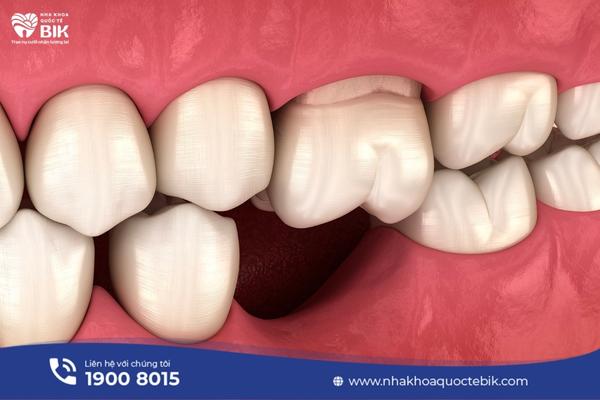
The jawbone is a part of the facial bone mass and is divided into the upper jawbone and the lower jawbone. In which, the upper jawbone is a spongy bone and is the main bone in the middle of the face, in contact with other bones to create the maxillary sinus, palate, skull base and nasal cavity. The lower jawbone is the lowest, largest and strongest bone in the facial skeletal system and is also the only bone in the skull that can move.
Jawbone resorption is a dental term that refers to the condition of the alveolar bone and the bone surrounding the teeth being degraded. The deterioration is clearly manifested through a lack of height, density, quantity and bone volume. Initially, bone resorption only appears in one location on the jaw, but over time, if not treated, it can progress to a more severe state and spread to adjacent bone areas, causing many serious consequences.
Both the upper and lower jawbones can easily be resorbed, greatly affecting the bite and facial structure.
2. Causes of jawbone resorption
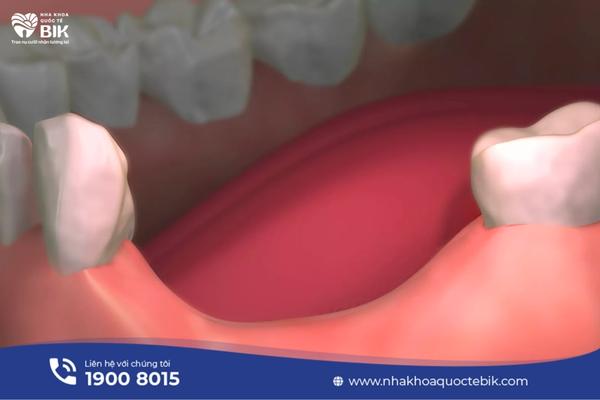
Tooth loss and periodontitis are the two main causes of jawbone loss:
2.1. Tooth loss
Tooth loss due to trauma or old age is the leading cause of jawbone loss. When a tooth is lost, it creates a gap at the location of the lost tooth root on the jawbone. Normally, the jawbone develops strongly and stably thanks to the forces exerted when chewing. When a tooth is lost, the force exerted at that location is no longer there, so the bone will gradually weaken and disappear.
2.2. Periodontitis
Periodontitis is a condition of severe inflammation and infection of the periodontal tissue and gums around the tooth root. Symptoms of periodontitis are bleeding gums, prolonged pain and red, swollen gums. In the long term, if not treated promptly, the gums will gradually become seriously damaged and will no longer be able to adhere tightly to the tooth root, creating favorable conditions for bacteria to invade and attack. At this time, bacteria will attack the soft tissues, causing the gums to recede, the tooth roots to be exposed, the tooth roots to be severely weakened, and eventually the bones and ligaments surrounding the teeth will also be damaged, causing the teeth to no longer have a place to support them.
3. How long does it take for the jaw bone to atrophy after tooth loss?
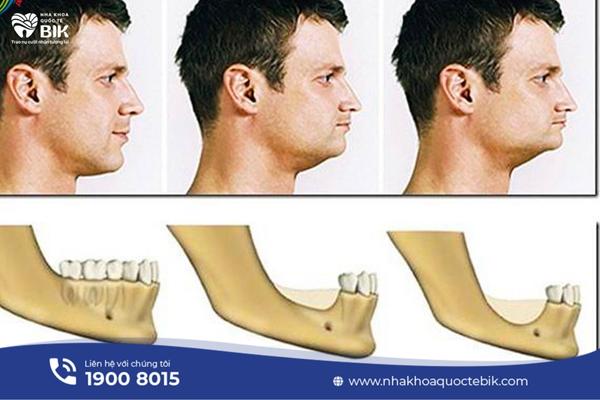
Normally, after losing a tooth for about 1 – 2 months, there are still no signs of jaw bone loss, this is the right time to take measures to prevent jaw bone loss.
Depending on each person’s constitution, jaw bone loss after tooth loss will occur quickly or slowly. After about 3 months, the jaw bone begins to show signs of deterioration, at this time the gums begin to sink, the adjacent teeth will gradually fall towards the gap in the jaw. The jaw bone will be 25% degraded after about 1 year of tooth loss and the face will gradually become unbalanced due to the lack of jaw bone support. After about 3 years, it is easy to see that both cheeks are clearly sunken because the jaw bone has now been degraded by 45% – 60%.
4. What are the types of jaw bone loss?
There are many forms of jawbone loss due to tooth loss:
4.1. Horizontal jawbone loss
In this form, the width of the jawbone at the location of the lost tooth root will narrow while the bone around that area will expand to fill the gap, so the adjacent teeth will tend to fall towards the missing tooth due to lack of bone support.
4.2. Vertical jawbone loss
With this form of jawbone loss, the jawbone at the location of the lost tooth will be sunken downward, deeper than the adjacent jawbone. In the long term, the gum area at the bone loss location will also shrink.
4.3. Bone loss in the sinus area
When the upper jaw teeth are lost for too long, the sinuses will lower and the sinus volume will gradually increase over time.
4.4. Bone loss of the entire face
When many teeth are lost in both the upper and lower jaws, bone loss of the entire face will occur. Signs of bone loss are also easy to detect because of obvious changes on the face such as sunken cheeks, sunken mouth, many wrinkles, etc.
4.5. Lowering the jawbone when losing many teeth
If in the long term, the jawbone loss is not treated promptly, the gradual loss of the jawbone will damage the nerve tubes deep below, making it difficult to perform denture restoration solutions.
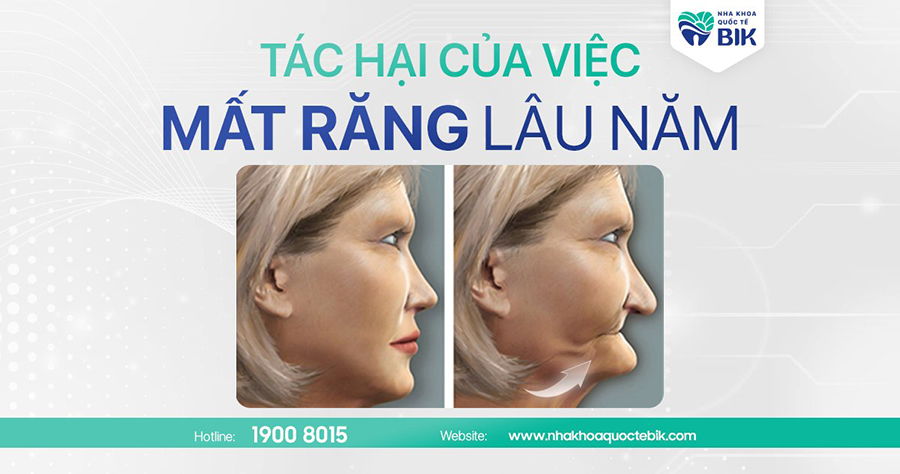
5. Effects of jawbone loss
Although jawbone loss does not occur immediately after tooth loss, when it occurs, it can lead to many consequences such as:
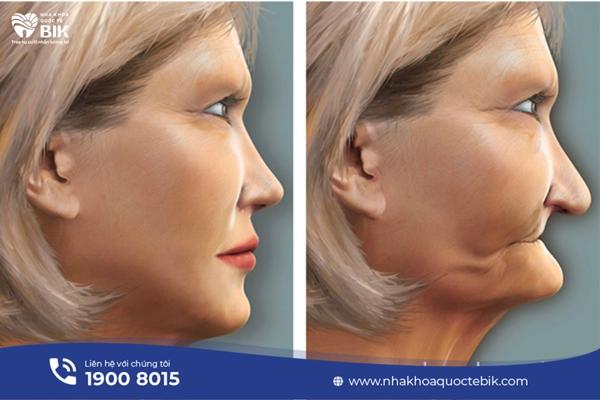
5.1. Effects on aesthetics

Jaw bone loss causes the lower jaw bone to become shorter, so the facial structure will be unbalanced, the skin will sag and the cheeks will be sunken inwards. When the jaw bone is lost to 60%, the signs of aging will appear more and more clearly, making the face look older than its age.
5.2. Difficulty in chewing
The jaw bone loss causes the jaw bone to fall lower and the teeth tend to fall towards the missing tooth root, leading to misaligned bites, making it difficult to chew.
5.3. Treatment obstacles
Because the jaw bone will be lost more and more if not treated promptly, it will cause more difficulties in the treatment process. At this time, the bone quality will not be qualified to perform dental implants. If you want to implant, bone grafting will be required, which takes more time and money.
5.4. Declining health

The jawbone is reduced, causing the width and height of the bone wall to be significantly reduced, no longer able to support the gums, causing the gums to recede, and also causing the gum line to gradually become thinner. This inadvertently creates an opportunity and a favorable environment for bacteria to grow and develop more, causing headaches, poor health and even sepsis.
6. Implant dentistry to prevent the risk of jawbone loss
It is necessary to have a good oral care regimen by having your teeth cleaned regularly every 6 months and going to the dentist for early treatment if there are signs of gingivitis. Ideally, immediately after tooth loss, you should implant dentistry to prevent jawbone loss most effectively.
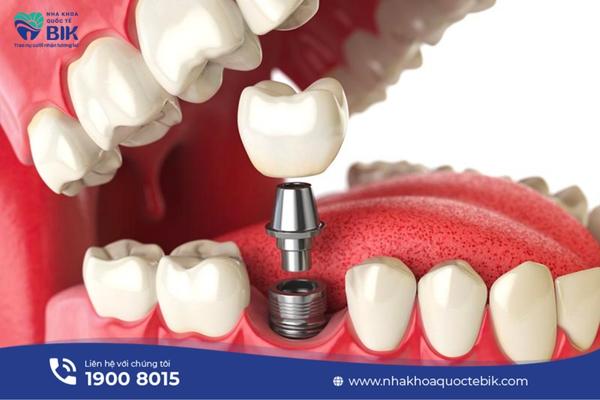
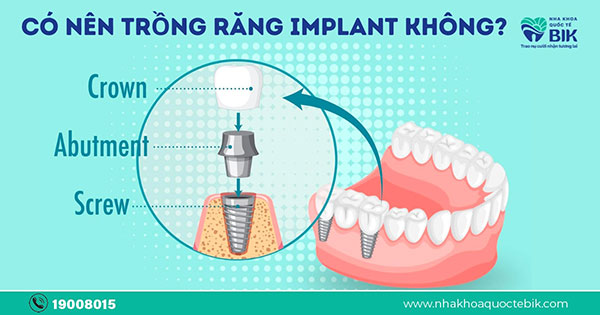
Dental Implant is a dental restoration solution that can be applied to both newly lost teeth and long-lost teeth. When performing dental implant, a titanium implant will be implanted into the position of the lost tooth and a porcelain crown will be attached on top like a complete tooth in both shape and function. The implant will now replace the lost real tooth root, the jawbone will develop normally and stably because it is still under constant pressure from the chewing process.
7. Can people with jaw bone loss get dental implants?
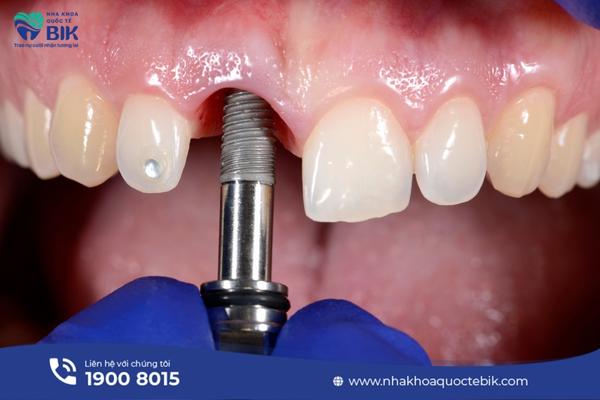
In cases where the jawbone has been reduced too much, simply implanting a tooth is not effective because the implant will certainly not be held firmly in the jaw and will be quickly eliminated.
However, the solution for this case is to perform a minor jawbone graft surgery before placing the implant to ensure the effectiveness of the tooth implant. Because the jawbone of people with jawbone loss is no longer healthy, tooth implantation will certainly be more complicated, depending on the condition of bone loss, the bone grafting time can last from 3-6 months and the complexity will also increase gradually.
There are 2 methods for bone grafting:
– Autologous bone grafting: Using the body’s bones such as the iliac crest, the lower jawbone, the chin or the jaw angle area.
– Artificial bone grafting: Using specialized grafting materials.
So jawbone loss does not occur immediately after tooth loss, but if left for a long time, the possible effects are very serious. Therefore, in any case, immediately after tooth loss, you should see a doctor to receive the clearest advice on solutions to prevent jawbone loss.