Periodontitis is a type of gum disease with a serious infection that affects the soft tissues around the teeth. You can easily recognize this disease through some signs of periodontitis and as soon as it is detected, you need to see a doctor immediately for timely treatment, preventing more serious effects on oral health.
1. What is periodontitis?
Periodont is an organization around the teeth including gums, alveolar bone, ligament system and has the function of supporting and keeping teeth strong in the jaw bone. Periodontitis is a gum disease that causes serious gum infection and affects the soft tissues surrounding the teeth.
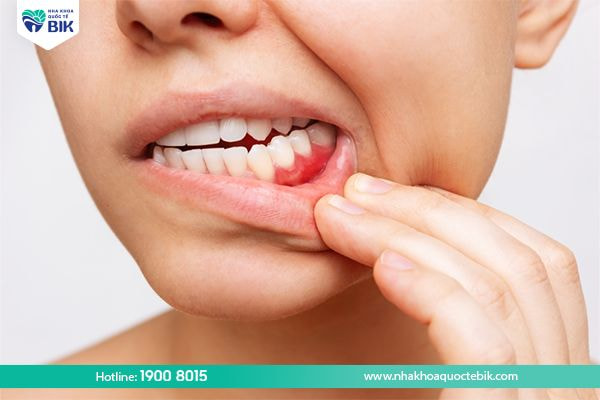
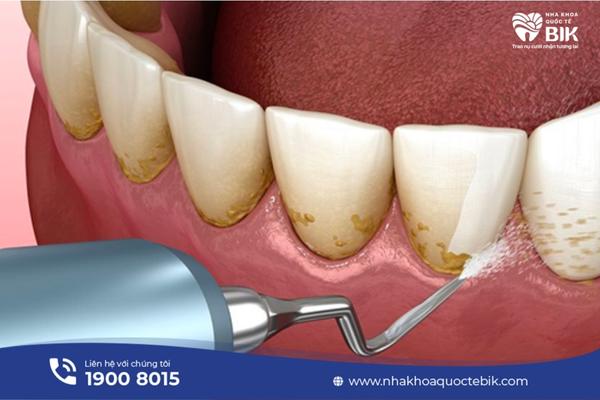
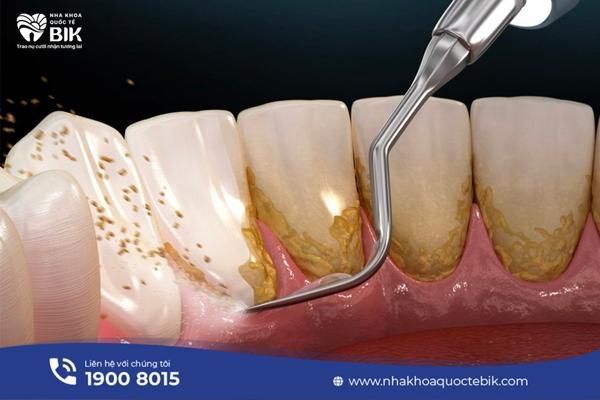
In fact, periodontitis is a more severe progression of the common gingivitis. Bacteria in food plaque metabolize sugar and create acids that erode tooth enamel and cause tooth decay. If you brush your teeth regularly and floss properly, you can prevent dental problems, but if you don’t clean them properly, plaque will gradually accumulate and turn into tartar. Bacteria in tartar will continue to have favorable conditions to attack, causing gum infection and leading to gingivitis.
If not treated promptly, plaque will spread further below the gum line. At this point, bacteria will create toxins and acids that cause chronic gingivitis and a more severe form of gingivitis called periodontitis. As periodontitis progresses, the gums will be broken down, creating conditions for bacteria to penetrate deeper, possibly even eroding the bone and causing the teeth to loosen.
2. Causes of periodontitis
Some common causes of periodontitis include:
– Improper oral hygiene causes food residue to accumulate over time, creating conditions for bacteria to grow.
– Not having regular dental check-ups to have tartar removed and general oral health checked.
– Regular use of stimulants such as alcohol, beer, and tobacco.
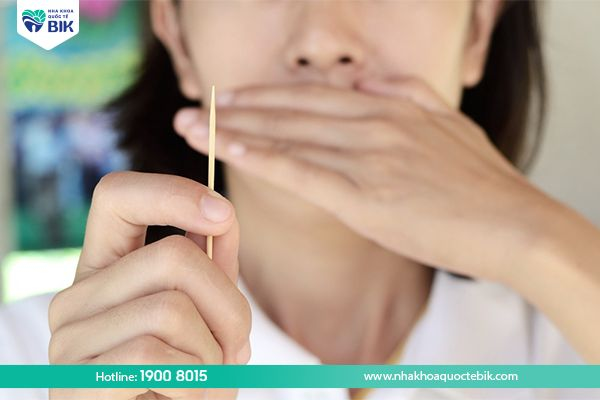
– Using toothpicks or sharp objects that are not hygienic to floss your teeth, causing inflammation, bleeding gums, exposed teeth, etc.
– Hormonal changes in pregnant women.

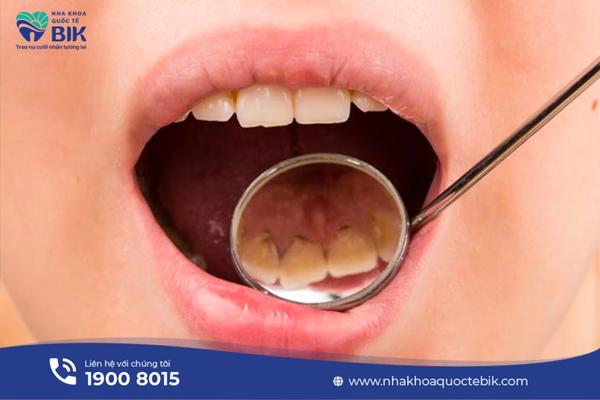
3. Signs of periodontal disease
Periodontal disease can be manifested by the following signs:
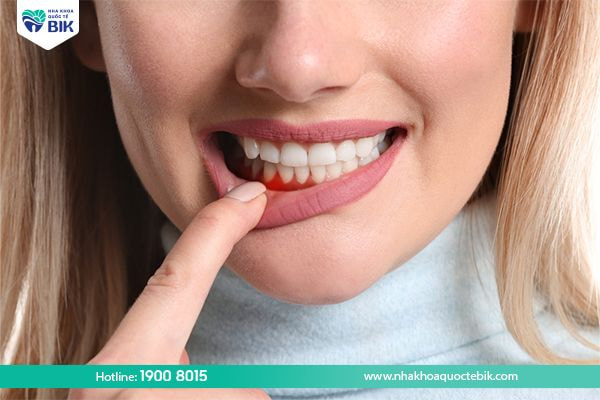
3.1. Swollen and bleeding gums
In the early stages of the disease, the gums will begin to swell and bleed. This symptom is not mild because it clearly shows that the gum tissue has been attacked and damaged. In case the swelling spreads to other areas, it means that the disease is progressing very quickly to the next stages.

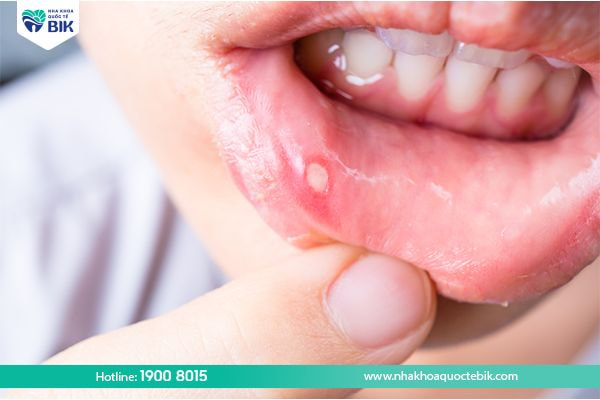
3.2. Mouth ulcers
If it is just a normal ulcer, it will heal in a short time, but if the mouth ulcer is caused by an infection, it will be much harder to heal. Moreover, this condition recurs, causing the patient to often feel pain and discomfort when eating and drinking.
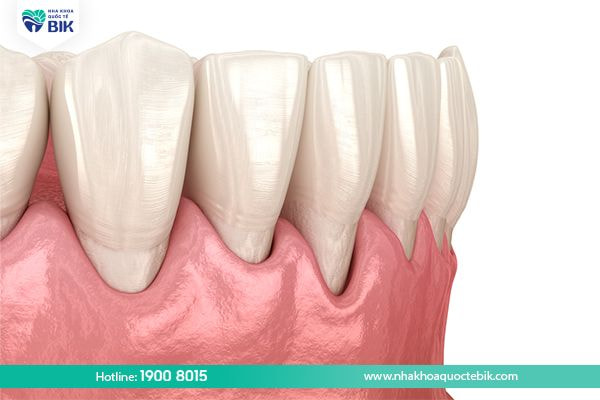
3.3. Gum recession
Gum recession is a sign that is quite difficult to recognize if the patient does not pay attention. However, if the patient regularly monitors and checks their oral health, they can easily feel the difference. Over time, the gums are pulled further and further away from the teeth, causing the tooth roots to become longer.
3.4. Loose teeth
When the gums and other soft tissues are damaged, the disease flares up. At first, the patient will only feel one tooth loose, but then the remaining teeth will also start to loosen. If not promptly treated, the patient may be at risk of permanent tooth loss.
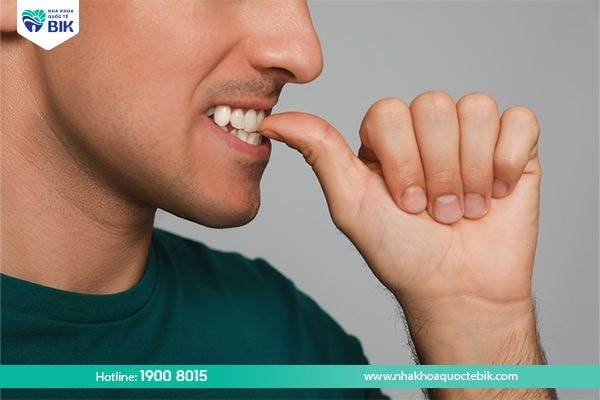

3.5. Pain when brushing teeth
At this time, the gums may begin to appear open wounds, causing the patient to feel pain and even bleeding when brushing teeth.

4. Effective treatment methods for periodontitis
Depending on each specific case, the doctor will prescribe the following methods to effectively treat periodontitis:
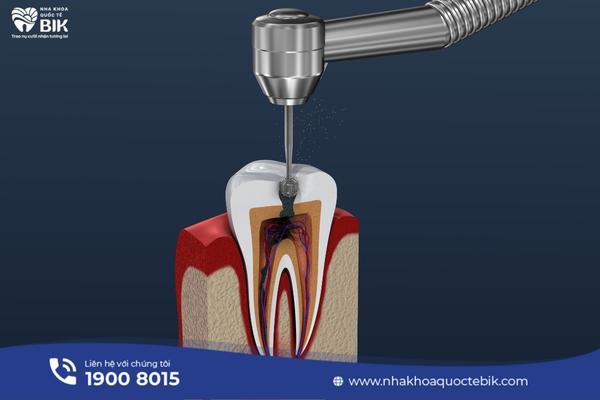
4.1. Non-surgical treatment
The doctor can treat periodontitis in the following ways:
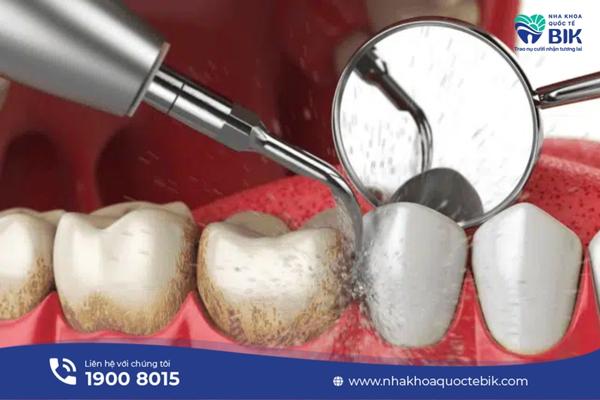
– Scaling and root treatment.
– Correcting or replacing fillings combined with cosmetic restoration.
– Having measures to fix loose teeth.
– If the tooth cannot be kept, the doctor will evaluate each specific case and prescribe tooth extraction,
– Using antiseptics and anti-inflammatory drugs.
Note that self-medication with anti-inflammatory drugs and antibiotics can help the abscess heal temporarily, but the disease does not end but progresses to a chronic state, sometimes with acute attacks and then recurs periodically and becomes more serious.
4.2. Surgical treatment
Surgical treatment will be applied when conventional treatment has been performed but is ineffective. The doctor will choose one of the following methods:
– Removing periodontal pockets: This method will help reduce the depth of the periodontal pockets, making cleaning and removing plaque easier.
– Regeneration: If the periodontal pockets are deep and have too many bacteria, it will further destroy the bone and periodontal tissue, and the teeth will even become loose at a serious level. After surgery, the bone and periodontal tissue will be regenerated.
– Soft tissue grafting: This method is applied in cases where the tooth root is exposed due to gum recession. Surgery will help restore and stop gum recession that destroys gum tissue as well as the tissues around the teeth.
5. Oral care to prevent periodontitis
You should note the following to effectively prevent periodontitis:
– Brush your teeth at least twice a day, especially after each meal to remove food plaque.
– Use a soft-bristled toothbrush with moderate brushing force to avoid damaging the gums.
– Use fluoride toothpaste to support healthy teeth.
– Replace toothpicks with dental floss to remove food debris between teeth, be careful to avoid affecting the gums.
– Maintain a scientific diet, supplement with all necessary vitamins and minerals to help increase resistance to help the body fight against bacteria harmful bacteria.

So you can recognize the disease completely easily based on some signs of periodontitis that BIK International Dental Clinic suggested above. As soon as the disease is detected, you should go to a reputable dental facility for examination, determine the specific infection status, and then proceed to completely treat periodontitis to avoid serious consequences later.