Tooth infection is an increasingly common disease today and can be easily recognized by obvious signs. When sick, customers will feel pain from mild to severe accompanied by discoloration of the gums due to attack. As soon as the disease is detected, patients need to go to dental facilities for timely examination to avoid dangerous complications that may appear later.
1. What is tooth infection?
Tooth infection, also known as tooth abscess, is a disease that originates from inflammation of the pulp and necrosis of the pulp, originating from the initial state of tooth decay that is not treated properly and promptly. Bacteria will attack the gums causing disease, and quickly spread to the adjacent teeth.
More dangerously, bacteria can enter the bloodstream and cause infection, encephalitis – meningitis, which is life-threatening, especially in patients with weak immune systems and pre-existing chronic diseases.
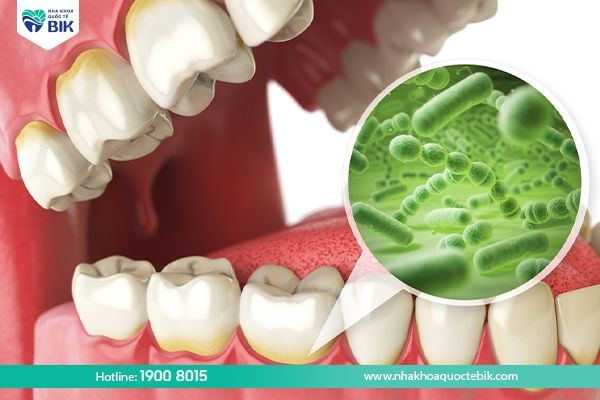
2. Signs of tooth root infection
Depending on the level of infection, the tooth will show different signs. Normally, people will tend to go to the dentist when the signs are clear such as prolonged toothache, swollen gums, etc. If observed, there will be many signs that help patients easily recognize tooth root infection:
2.1. Prolonged toothache
Prolonged toothache is the most typical symptom of tooth root infection. At the infected gum area, there will be mild to severe pain, dull pain lasting for many days without stopping. The pain can even spread to other areas such as the jaw, ear, temple, head.
If the patient is subjective and does not go to a dental facility for treatment but lets the gum infection become severe, causing the painful areas to spread, and the location of the tooth pain cannot be determined, then an X-ray is needed to accurately diagnose the location of the infected tooth.

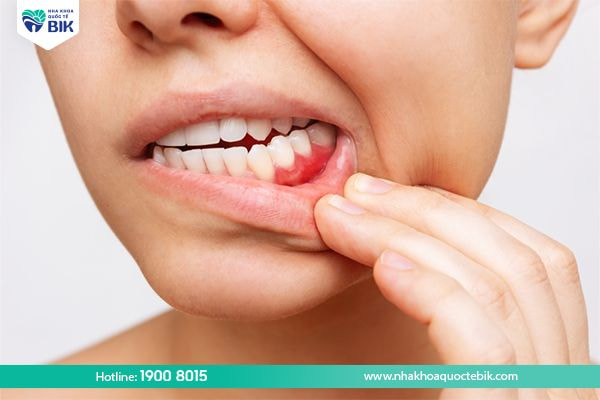
2.2. Pus and swelling of the gums
Pus and swelling of the gums are another common sign of a tooth infection. When the tooth is painful, the gums will change from the initial light pink color to dark red, swollen or more severe, pus. If the pus is not treated promptly, it can burst, creating a favorable environment for bacteria to grow, causing bad breath.
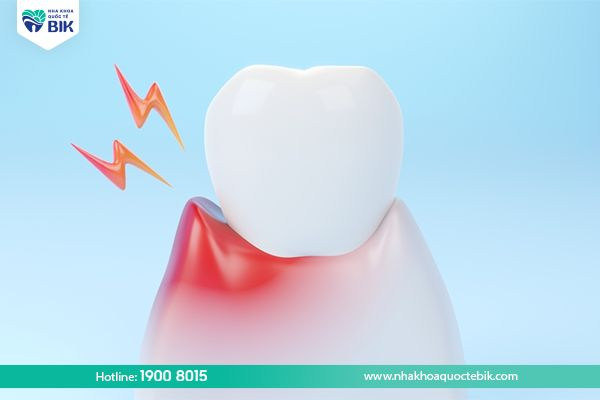
2.3. Teeth become more sensitive
When the tooth is infected, the gums will become more sensitive than usual, especially when there is a change in the temperature of food. At this time, customers will feel sensitive and uncomfortable when eating foods that are too hot or too cold. In addition, foods containing a lot of sugar also cause irritation and prolonged toothache.
2.4. Discolored teeth
The infected tooth location will often change from the original bright white blood to dark brown or gray. The reason for tooth discoloration is that the dead pulp produces toxic, rotten substances that stick to the tooth surface through small holes in the tooth.
2.5. Swollen lymph nodes in the neck
Swollen lymph nodes in the neck are also one of the symptoms to recognize tooth root infection. The infection can spread to surrounding areas, especially when the patient does not go to a reputable dental clinic for treatment. The locations that can be affected are the sinuses, jaw or lymph nodes under the jaw and neck. These nodes can cause swelling and pain for the patient.
2.6. High fever
In addition to the above symptoms, the patient may also have fever, headache, nausea, fatigue, etc. When experiencing the above cases, customers should not take antipyretics or painkillers to avoid affecting their overall health. When the body temperature rises above 38 degrees Celsius, go to the nearest medical facility for examination and treatment.

3. Consequences of toothache infection
When visiting reputable dental clinics, toothache infection can be treated quite easily. However, in some cases, if the patient is not examined promptly, serious complications can occur. Most complications arise due to untreated bacterial infection:
– Tooth loss: When the infection develops severely, it goes from the tooth root into the jawbone and spreads to the surrounding soft tissues. If not treated with proper measures, the patient may have to remove the infected tooth.
– Odontogenic cyst: When gum infection is not effectively treated, a fluid-filled cavity can develop under the tooth root.
– Maxillary sinus infection: This can occur if the tooth carries disease-causing bacteria from the upper molars that are located near the sinuses.
– Infective endocarditis: When bacteria carry disease through the blood vessels, it can lead to bruising and infection, the most dangerous of which can lead to death.
– Ludwig Angina: This is a very serious infection that spreads to both sides of the tongue, jaw, and chin and can be fatal. This condition is common in adults, the main cause of which is untreated tooth infection.
– The biggest danger is that gum infection can develop into a blockage of the airway and cause suffocation and can even lead to death.
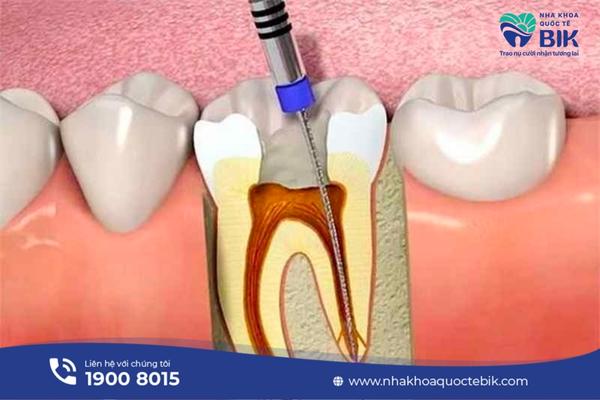
4. Treatment of tooth root infection
Treatment of tooth root infection will depend on the condition of the disease as well as the health status of the infected person. However, there are common measures commonly used to treat infected teeth as follows:
4.1. Treating tooth root infection at home
Customers can use diluted salt water to rinse their mouths, this method can temporarily relieve pain but cannot cure the infected tooth. Or you can use pain relievers to prevent the infection from spreading to the healthy teeth next to it. However, note that you should not use any medicine without a doctor’s prescription.

4.2. Treatment of tooth root infection at the dentist
To be treated thoroughly, patients need to go to reputable dental facilities for timely and proper examination, avoiding future complications.
The goal of treating tooth root infection is to eliminate the infection but to protect the teeth as much as possible. Customers will first have a general examination and X-ray to assess the level of tooth root infection and then come up with a reasonable treatment plan.
The doctor will perform an incision to drain the pus from the tooth. In some cases, patients will have root canal treatment, fillings, and porcelain tooth restorations to preserve the teeth. If the inflammation is too severe, the tooth will be extracted to avoid spreading to the healthy teeth next to it.
5. How to prevent tooth root infection?
To prevent tooth root infection, you should note the following:
– Brush your teeth at least twice a day, especially after each meal to remove food plaque.
– Use a soft-bristled toothbrush with moderate brushing force to avoid damaging the gums.
– Replace the toothbrush every 3-4 months to avoid bacteria accumulation.
– Use a suitable toothpaste to help keep gums healthy.
– Replace toothpicks with dental floss to remove food debris between teeth, avoiding damaging the gums.
– Maintain a scientific diet, supplement with all the necessary vitamins and minerals to support increased resistance to help the body fight harmful bacteria.
– Visit the dentist regularly at least every 6 months to ensure regular oral health checks.
So periodontal infection is a condition in which the tooth is infected in the gums. If not examined and treated promptly, the inflammation will spread to the surrounding areas, causing dangerous complications for the patient. To treat periodontal infection effectively and safely, you can choose to go to BIK International Dental Clinic to be properly treated by a team of doctors with expertise and extensive experience in the profession.