Gingivitis or gum infection can cause swollen gums. To improve this condition, you need to practice proper oral hygiene or follow your dentist’s instructions. Read on to learn more about the causes of swollen gums, complications, and how to fix them.
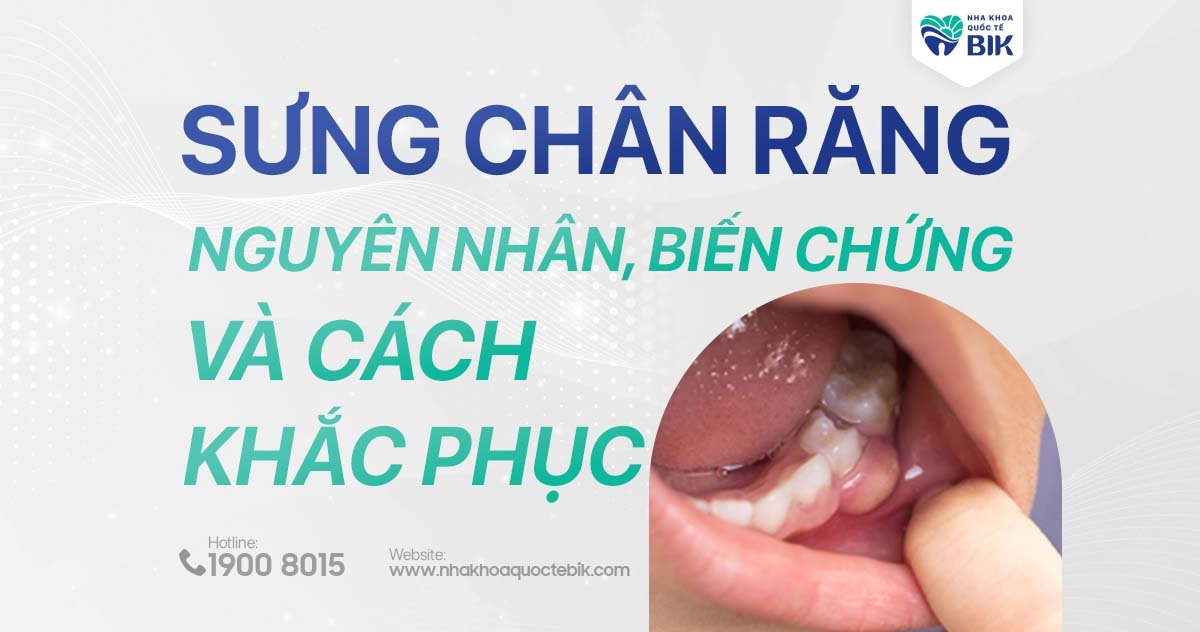
What is swollen gums?
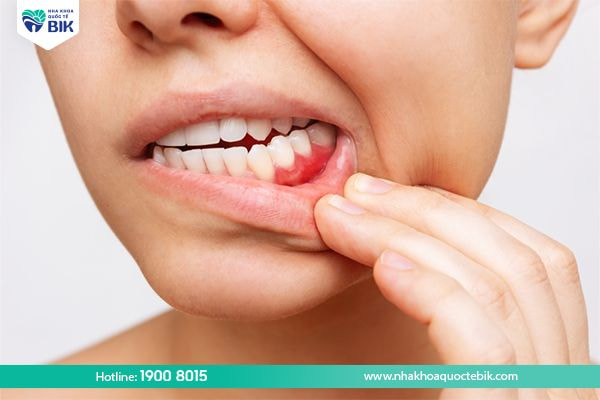
Swollen gums or periodontitis is a condition in which the tooth pulp or gums are attacked by bacteria, causing infection and forming pus pockets at the root of the tooth. Swelling and inflammation of the structures around the tooth root, even with pus, are the most obvious signs of this disease.
If not treated promptly, this inflammation can cause serious consequences for oral health and lead to loose and broken teeth. This disease can occur at any age, even in children as young as 1-2 years old.
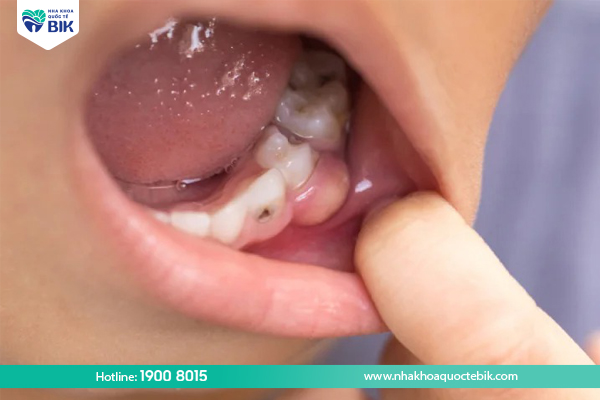
Causes of swollen gums
Swollen gums can occur for a number of reasons:
Swollen gums due to gingivitis, periodontitis
Gingivitis causes irritation in the gum area, leading to swelling, redness and pain. The initial symptoms are often ignored and not treated promptly. When the situation becomes more serious (such as swollen gums with pus), many people seek treatment. In more severe cases, periodontitis can occur or even cause tooth loss.
Gingivitis occurs due to improper oral hygiene, causing bacteria and food plaque to accumulate between the teeth, deep under the gums and cannot be completely removed. If you do not clean your teeth regularly, hard plaque will gradually form that is difficult to remove with normal dental hygiene.
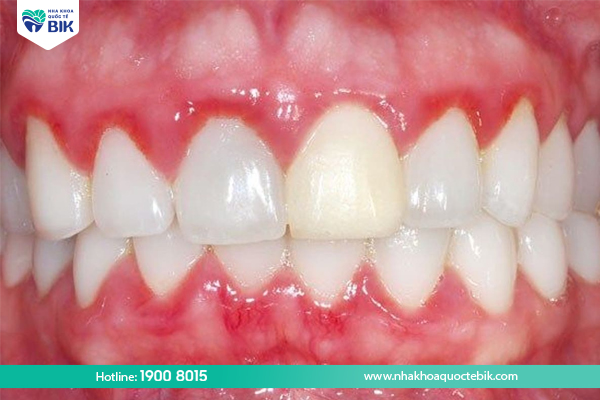
Swollen gums during pregnancy
During pregnancy, hormones in a woman’s body undergo many changes, leading to increased blood flow to the gums and making them more susceptible to irritation. At the same time, hormonal changes also reduce the ability to produce Prostaglandin – a natural anti-inflammatory fatty acid. Therefore, the risk of gingivitis and swollen gums during this period will be higher than normal.
Due to lack of nutrients
Another reason for swollen gums is due to nutritional deficiencies. Vitamins, especially the B and C vitamins, play an important role in maintaining oral health. When the body lacks Vitamin C, there is a risk of scurvy and swelling of the gums.
Swollen gums due to infection
Swollen gums caused by fungi and bacteria, leading to gingivitis and gum infection. This is a common condition in both adults and children, which can lead to pus in the tooth root, progressing to tooth abscess and swollen gums.
Treating severe pus-filled gingivitis will be more complicated and difficult than when it is first detected, so treatment should be started as soon as possible to prevent the condition from becoming more serious.
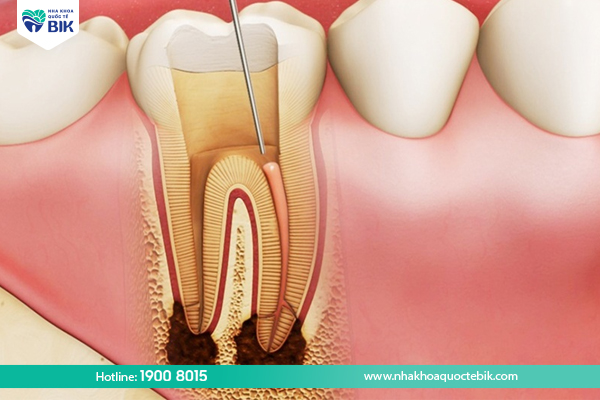
Pulmonary inflammation
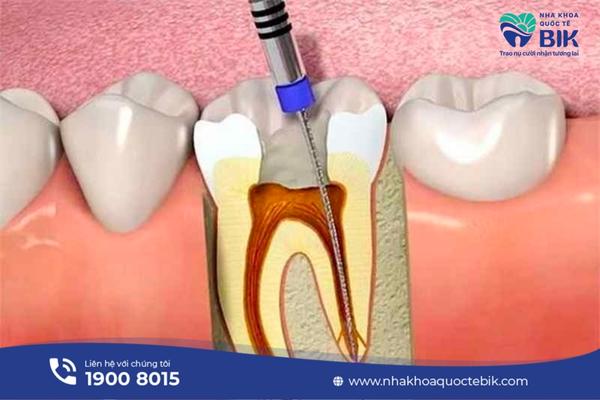
Teeth can decay due to many causes such as trauma or prolonged infection around the tooth, spreading to the root area and affecting the inner pulp. Bacteria from cavities can penetrate deep into the tooth pulp. The larger the cavity, the easier it is for bacteria to penetrate and come into contact with the oral environment.
Bacteria can penetrate vertically through the tooth or cause trauma to the pulp, leading to inflammation and pulp death. If pulpitis persists, the infection can spread down to the root of the tooth, causing an abscess. This is a serious stage of the disease.
If not treated promptly, the infection in the root of the tooth can spread to the entire root and even to other teeth, forming an abscess and leading to jawbone loss, loose teeth and extraction. The most dangerous thing is when bacteria from the abscess spread into the blood, causing sepsis and can be life-threatening.
Gingivitis due to teething
This is a phenomenon that occurs when children are teething, but it is only temporary. The teething process causes food to stick and create bacterial plaque. In severe cases, it can cause swollen tooth roots. Often occurs in teeth number 6 and 7.
Some other reasons
There are other causes of swollen gums such as: Teeth growing in the wrong position, teeth damaged by collision, smoking, hormonal changes, diabetes, weakened immune system, etc.
Complications that can occur when the gums are swollen
In the mild stage
At this time, the problem does not cause much pain, so the patient can still eat and drink and function normally. If you know how to properly care for and clean your teeth, combined with a scientific diet, the gums will quickly recover without the need for any dental intervention.
In the severe stage
When subjected to physical impact, even mild, it causes pain and discomfort to the patient. When this happens, the oral condition will become more serious. Therefore, you should not eat food that is too cold or too hot because it can damage the gums and cause more severe pain. If left for a long time, it can lead to bleeding gums, gingivitis and swollen gums with pus, which is a very dangerous condition for your health.
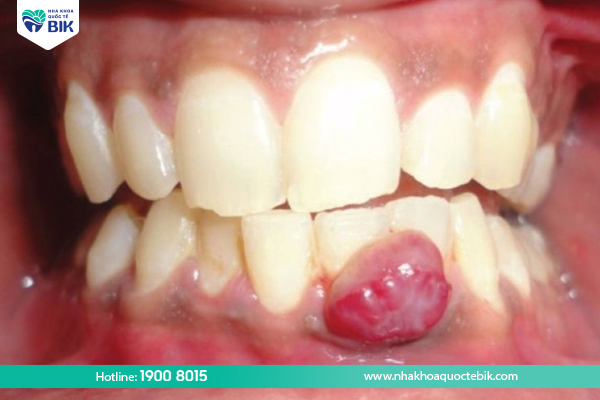
What to do if your gums are swollen?
Most cases of swollen gums can be improved through self-care at home. Specific measures include:…
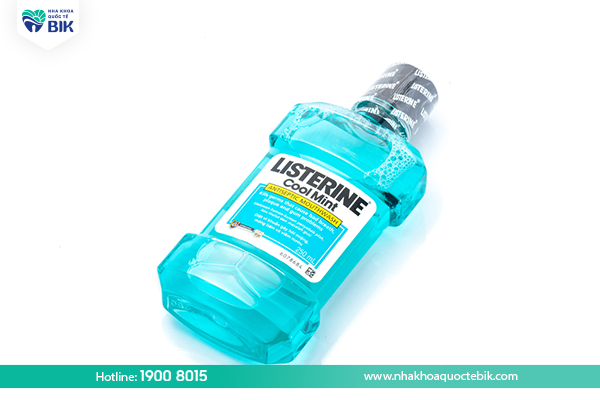
Use antibacterial mouthwash
Mouthwash containing antiseptics can limit the growth of bacteria and plaque in the mouth. People with gingivitis can use a mouthwash containing cetylpyridinium chloride to kill bacteria. If necessary, your doctor may also prescribe a mouthwash containing chlorhexidine to eliminate harmful bacteria in the mouth.
Herbal Mouthwash
There are several studies that have confirmed that the use of herbal mouthwashes, such as those containing tea tree, clove, and basil essential oils, has anti-inflammatory effects. They are effective in preventing bacteria and reducing inflammation. Using herbal mouthwashes for 21 days can help reduce swollen gums and support oral health. In addition, some herbal mouthwashes can also remove plaque and treat gingivitis at home.
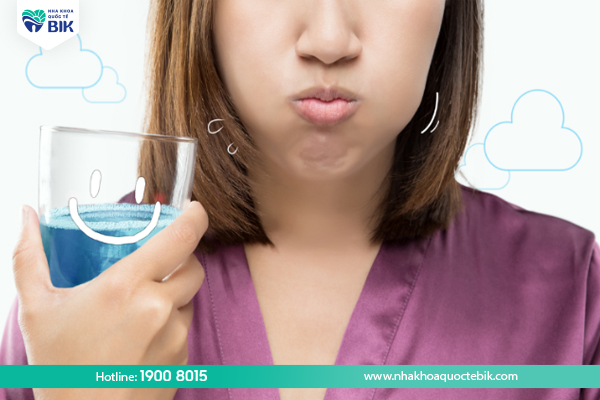

Rinse with salt water
To heal gum injuries, you can use a salt solution to rinse your mouth. Researchers have confirmed that rinsing your mouth with a 1.8% salt solution for two minutes, three times a day can help speed up the healing process of gum injuries.
One way to make a strong salt solution is to dissolve a teaspoon of salt in a cup of boiled and cooled water. Use this solution to rinse your mouth 2-3 times a day to reduce gum swelling and improve the condition of the injury.
How to treat swollen gums at the dentist
In cases of severe gum swelling, especially swelling in the wisdom tooth area, it may be necessary to apply clinical treatments to avoid unwanted situations. Specific clinical treatments include:…
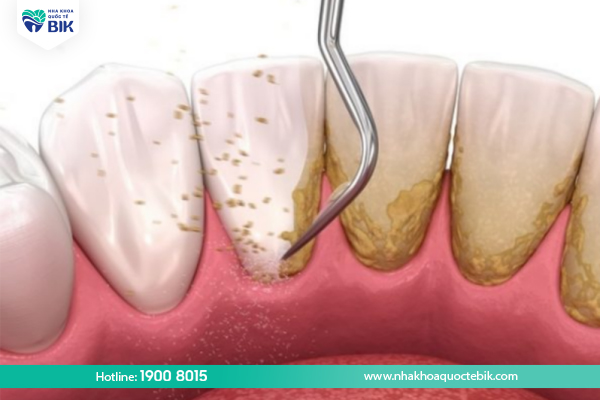
Scaling
Scaling is a professional method to remove tartar, plaque and support the treatment of gingivitis. During scaling, the dentist uses special equipment to remove tartar. The dentist will then polish the tooth surface to help prevent plaque buildup.
Incision of abscess
In cases of severe swelling of the tooth root due to abscess, the doctor may also recommend an incision to remove the pus. After the incision, the doctor will clean the area with a special solution.
Pulpectomy
In cases of severe infection, the doctor may recommend a root canal to remove the bacteria causing the inflammation. The doctor will then treat it by filling the tooth or placing a specialized material or porcelain crown.
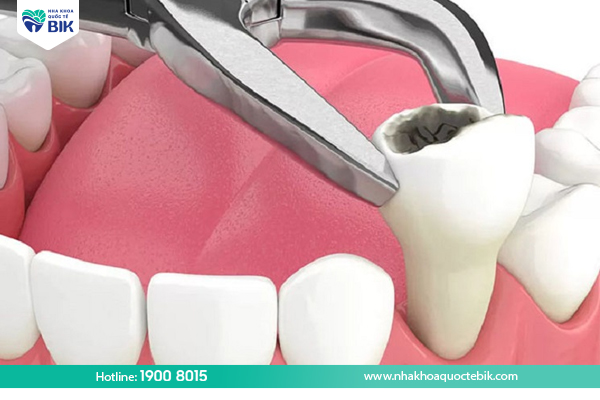
Tooth Extraction
If gingivitis is associated with a serious tooth infection, your dentist may also recommend tooth extraction to treat the condition and prevent the spread of infection.
Take Painkillers
Painkillers such as ibuprofen can help relieve pain from a tooth abscess or periodontitis. Oral antibiotics are often used to kill bacteria. Other interventions may also be needed to treat a tooth abscess.
How to Prevent Swollen Gums?
Gingivitis can be prevented by practicing good oral hygiene and following your dentist’s instructions. To minimize gum swelling, you can take the following care steps:
- Brush your teeth properly twice a day with a soft-bristled toothbrush and do not brush too hard to avoid damaging the gums.
- Use dental floss to clean plaque between teeth, gently so as not to damage the gums.
- Rinse your mouth with diluted salt water to remove bacteria and effectively prevent infection.
- Drink enough water to stimulate saliva secretion to help remove bacteria.
- Avoid hot, cold foods, strong mouthwashes, alcohol and tobacco because they can irritate gums.
Gingivitis will affect your oral health. Take care of your teeth properly and have regular dental check-ups every 6 months to avoid gingivitis and swollen gums. If you need advice, contact BIK International Dental Clinic for support!