Periodontitis is a fairly common oral disease caused mainly by patients not practicing proper oral hygiene for a long time. This causes plaque to form, creating a favorable living environment for bacteria to grow and attack the gums and teeth, causing disease. Is periodontitis contagious? is a question of many people, let’s find out with BIK International Dental Clinic in the article below!
1. Causes of periodontitis
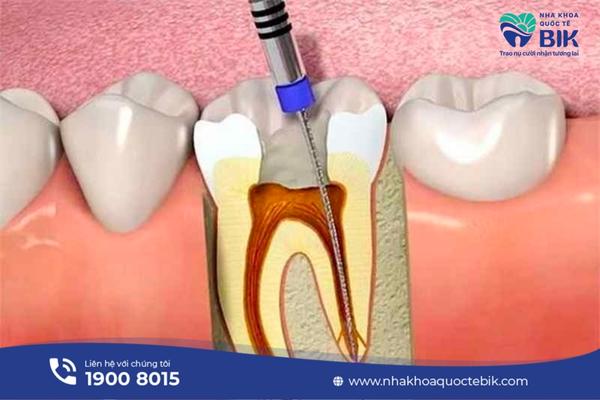
In fact, periodontitis is a more severe progression of common gingivitis if not treated promptly. The main cause of periodontitis is poor oral hygiene, creating conditions for bacteria to accumulate in tartar plaque. These plaques often exist between the tooth root and the gum, at which point bacteria will easily attack, causing gingivitis, breaking down the tissue structure, making the gum not firmly attached to the tooth root.

In addition, some other causes of periodontitis include:
– Hormonal changes during pregnancy make the gums more sensitive and increase the risk of gingivitis.
– Some diseases such as cancer, weakened immune system, diabetes, etc. increase the risk of infection.
– Patients use certain medications that reduce saliva flow while saliva itself is a factor that protects teeth and gums.
– Family history of oral diseases.
2. What are the effects of periodontal disease?
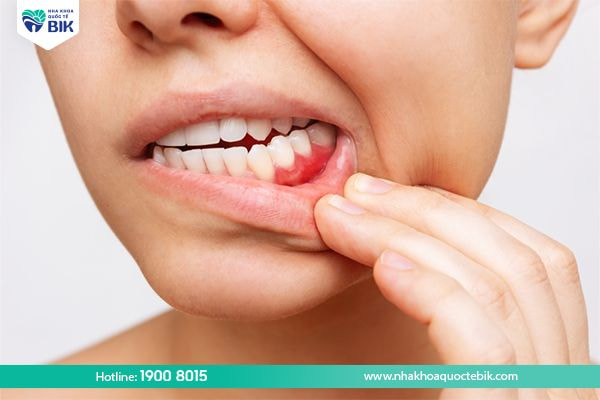
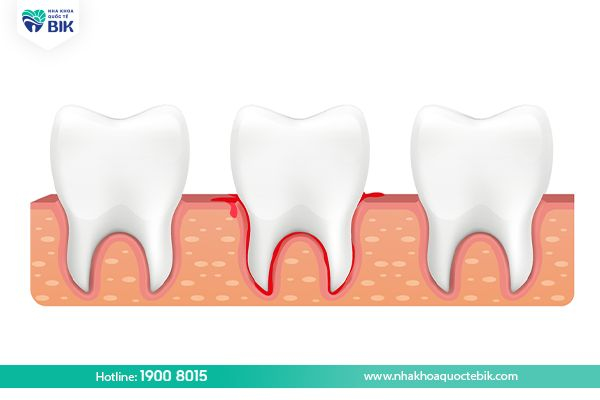
Periodontal disease can be easily recognized by the following signs:
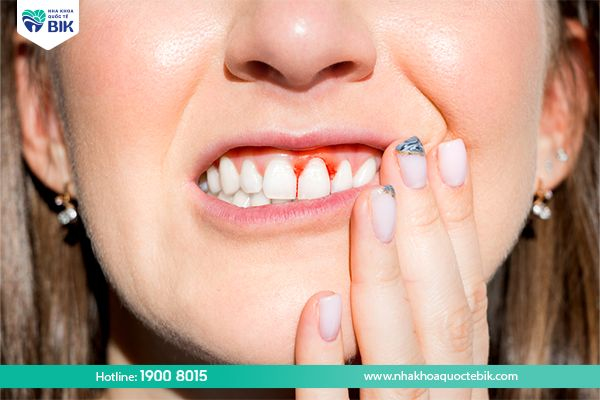
– Gums are dark red or bright red with swelling and pain.
– Gums bleed easily.
– A gap or pus pocket appears between the gums and teeth.
– Teeth become longer or less firm because the tissues have been broken down.
– Pain and discomfort when chewing.
– Bad breath.
Basically, the main function of the periodontium is to support and protect the teeth, so if this part is infected or severely damaged, the risk of the patient’s teeth becoming loose or falling out is very high. Not only that, periodontal disease also causes other effects on overall health because bacteria can invade and attack other organs such as the heart, lungs, bronchi, etc. From there, the patient may encounter problems with bones and joints, coronary arteries, breathing or even stroke.
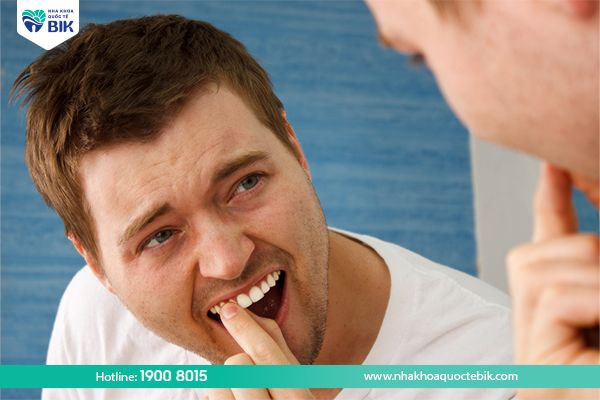
3. Is periodontitis contagious?
Periodontitis is actually a more severe progression of gingivitis as mentioned above. In the early stages of gingivitis, the gums will show signs of swelling, redness, softness and easy bleeding, but this is often not noticed because this does not make the patient feel too uncomfortable.
When gingivitis becomes more severe, it will also be easier to recognize through specific manifestations. According to experts, both children and adults of all ages are at risk of periodontitis and this bacteria can be spread through saliva. This means that the risk of infection of this disease to family members when living together is very high.
4. How to treat periodontitis?
For each stage of the disease, the doctor will prescribe different appropriate treatment methods:
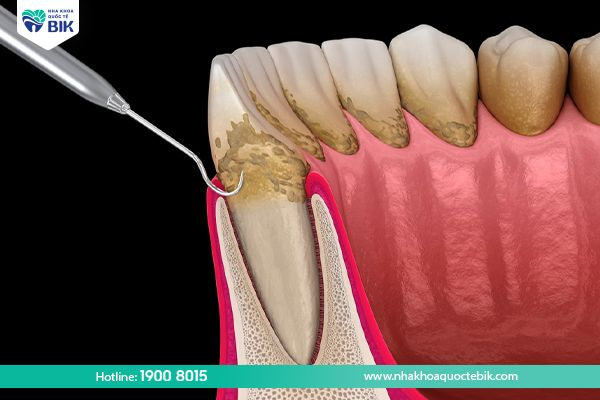
4.1. Treating periodontitis in the early stages
At this time, periodontitis can be treated by scaling to remove the living environment of bacteria, protecting the gums and teeth from further damage. In cases where periodontitis is a little more severe and plaque is difficult to clean normally, the doctor will perform a bottom cleaning or root planing to ensure effective treatment.
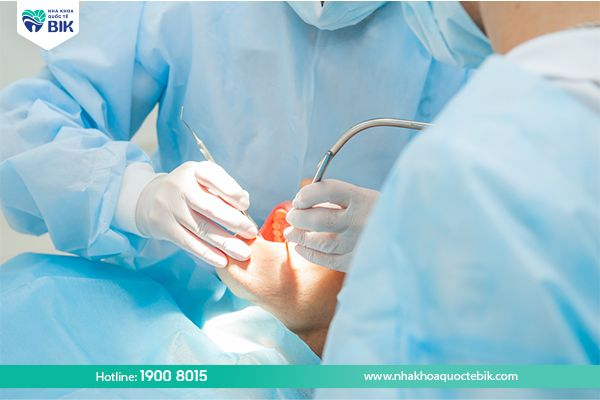
4.2. Treatment of severe periodontitis
In cases where periodontitis has progressed to a severe stage when the pus pockets have penetrated deep into the teeth and gums, the doctor needs to perform surgery to completely clean the tooth roots and remove the pus pockets. Then, if there is a lack of gum, a gum graft will be performed.
In some cases of periodontitis where the gums and tooth sockets have been partially damaged, the doctor will apply certain surgical techniques to support the regeneration of these tissues. In addition, in cases of severe periodontitis that cannot retain real teeth, the doctor will advise the patient to perform an implant or a porcelain bridge restoration to restore aesthetics as well as chewing ability.
So the answer to the question of whether periodontitis is contagious is that it can be transmitted through saliva. Therefore, whether children or adults, once periodontitis or gingivitis is detected, they need to go to the dentist for examination and prompt treatment to avoid serious consequences later.