Chronic periodontitisis a fairly common oral disease today. This disease causes serious damage to the tissues around the teeth, making it difficult to chew and perform daily activities. In addition, bacteria from the oral cavity can invade other parts of the body, causing other systemic health problems.
1. Symptoms of chronic periodontitis
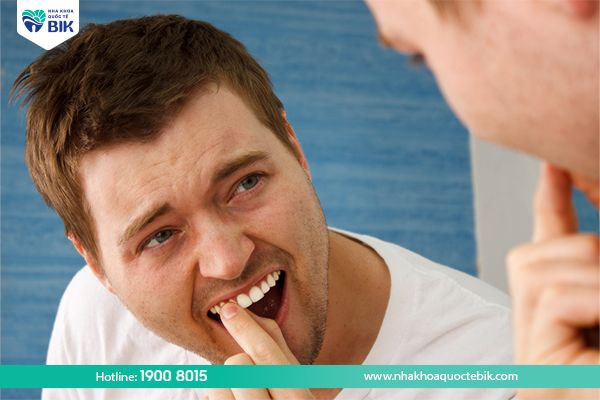
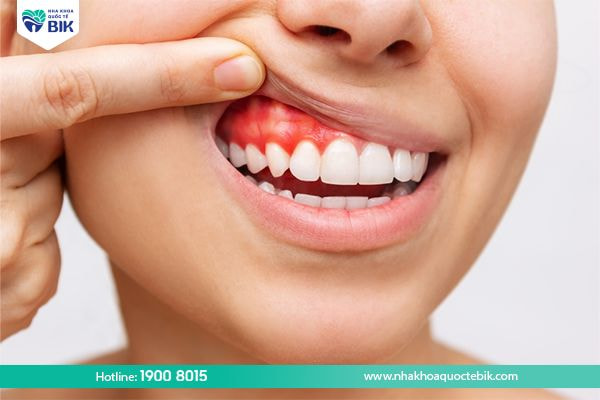
Chronic periodontitis is an oral disease that has a rather complicated progression and originates from common gingivitis when not treated promptly. If you detect the following symptoms, you should go to the dentist for examination as soon as possible:
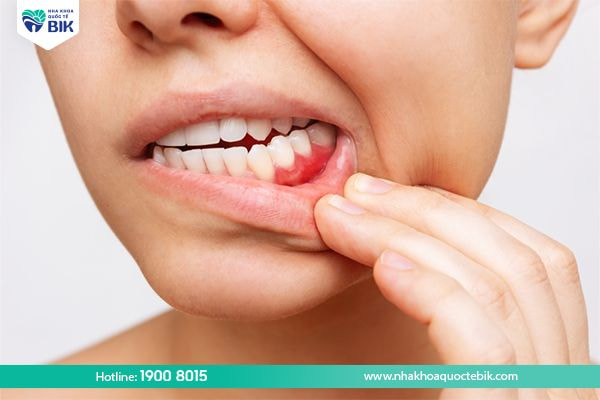
– Gums change from pink to dark red or bright red.
– Gums are swollen, painful when exposed to food that is too hot or too cold.
– Teeth become sensitive and vulnerable to the impact of toothbrushes or when chewing normally.
– Dense plaque appears.
– Formation of periodontal pockets containing pus inside.
– Bad breath.
– Loose teeth, increased distance between teeth causing teeth to gradually become sparse.
2. Causes of periodontitis
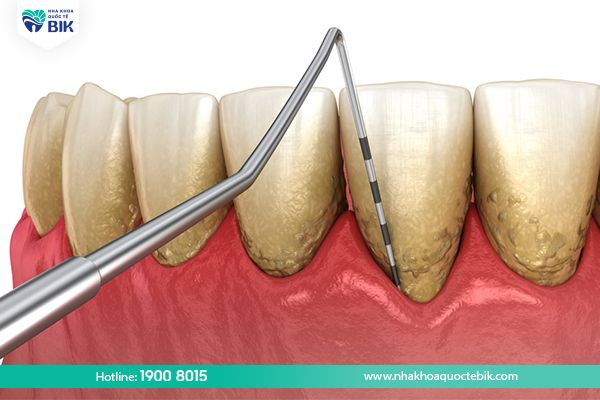
Patients with chronic periodontitis are mainly due to poor oral hygiene, causing food plaque to remain on the tooth surface. Over time, these plaques will calcify into tartar and become an extremely favorable environment for bacteria to grow.
Bacteria will then attack the teeth and gums, causing inflammation and then begin to form pus-filled pockets. These pockets of inflammation combine with tightly adhered tartar, so patients cannot remove them at home and need to go to the dentist.
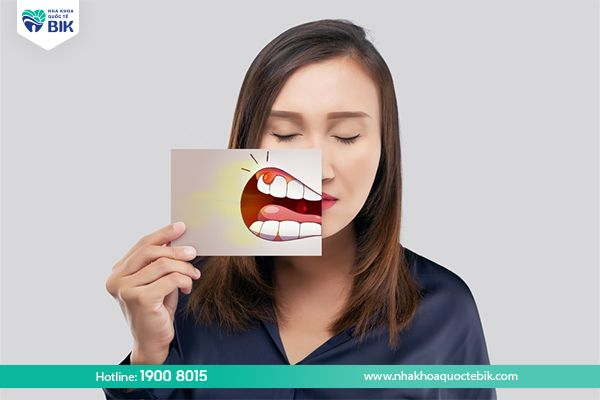
In addition, some other causes of periodontitis include:
– Hormonal changes during pregnancy in women make the gums more sensitive and increase the risk of gingivitis.
– Some diseases such as cancer, weakened immune system, diabetes, … increase the risk of infection.
– Patients using certain medications reduce saliva flow while saliva itself is a protective factor for teeth and gums.
– Family history of oral disease.
3. What are the effects of chronic periodontitis?
Chronic periodontitis is a serious disease, the gums can bleed and directly affect the alveolar bone. On the other hand, the formation of pus pockets will create favorable conditions for bacteria to grow more strongly and cause the following effects:
– Damage to the tooth socket makes the tooth no longer stable on the jaw, can become loose and fall out.
– Pregnant women with periodontitis may increase the risk of premature birth or low birth weight.
– Bacteria in the oral cavity have been shown to be associated with heart disease, arterial blockage and even stroke.
– The incidence of chronic periodontitis is often higher in people with diabetes and this disease also makes it more difficult to control blood sugar.

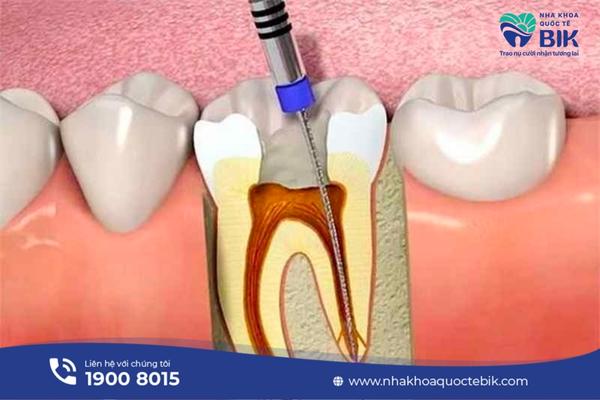
4. How to treat chronic periodontitis?
Depending on the level of infection, the doctor will prescribe the appropriate treatment method:
4.1. Emergency treatment
Emergency treatment of periodontitis occurs when an abscess appears in the gum area or the mucosa is inflamed. Touching the pus pocket causes more or less pain depending on the specific condition. At this time, the doctor will prescribe antibiotics and anti-inflammatory drugs, but in general, this is only a temporary method, the disease can progress to chronic and recur acutely.

4.2. Non-surgical treatment
Depending on the specific condition of periodontitis, the doctor will prescribe some of the following methods:
– Apply anti-inflammatory and antiseptic drugs to the swollen and inflamed gums.
– Scaling teeth to remove the living environment of bacteria.
– Check fillings, correct or replace fillings, restore teeth that have been filled incorrectly.
– Fix loose teeth.
– Extract teeth in cases where real teeth cannot be kept.
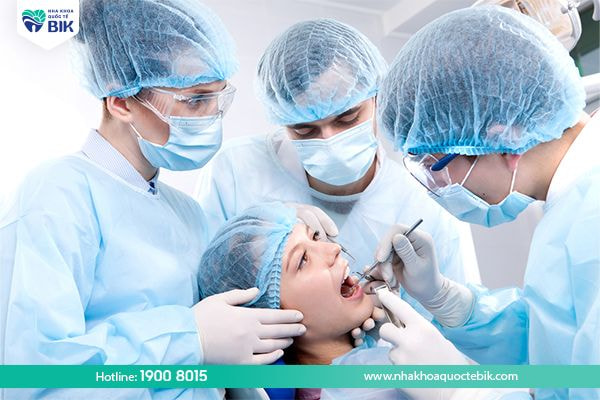
4.3. Surgical treatment
Surgical treatment is performed in cases where other measures have been taken but are ineffective:
– Removing periodontal pockets: The doctor will reduce the size of the periodontal pockets to facilitate cleaning of plaque on the teeth.
– Reconstructive surgery: Periodontal pockets are formed due to the destruction of periodontal tissue and bone. When these pockets become deeper, they will cause the teeth to become loose. Destroyed periodontal tissue and bone can be regenerated after removing the periodontal pockets.
– Soft tissue grafting surgery: Periodontal inflammation causes gum recession and exposes the tooth roots, so soft tissue grafting surgery is performed to restore the affected tissue around the teeth.
4.4. Maintenance treatment
Periodontitis treatment needs to be maintained when the disease is stable. Patients need to have regular check-ups according to the doctor’s appointment, regularly monitor to promptly detect and prevent the disease from recurring and silently progressing.
5. Oral care to prevent periodontal disease
– Clean your teeth twice a day, especially after eating to remove food residue on the tooth surface.
– Use a soft-bristled toothbrush with moderate brushing force to avoid damaging the gums.
– Use fluoride toothpaste to support healthy teeth.
– Replace toothpicks with dental floss to remove food debris between teeth.
– Maintain a scientific diet, supplement with necessary vitamins and minerals to support increased resistance to help the body fight harmful bacteria.
– Visit the dentist regularly at least twice a year to ensure regular check-ups of oral health.

So chronic periodontitis can be recognized through the signs that BIK International Dental Clinic suggested above. As soon as you notice the symptoms, you should go to a reputable dental facility as soon as possible for examination and timely treatment to avoid other serious effects.