Purulent periodontitis is an infection in the oral cavity that usually concentrates in the gum area or spreads to other parts of the mouth. When the gums are inflamed, it is a sign that your oral health is having a serious problem and needs to be treated immediately to avoid dangerous complications.
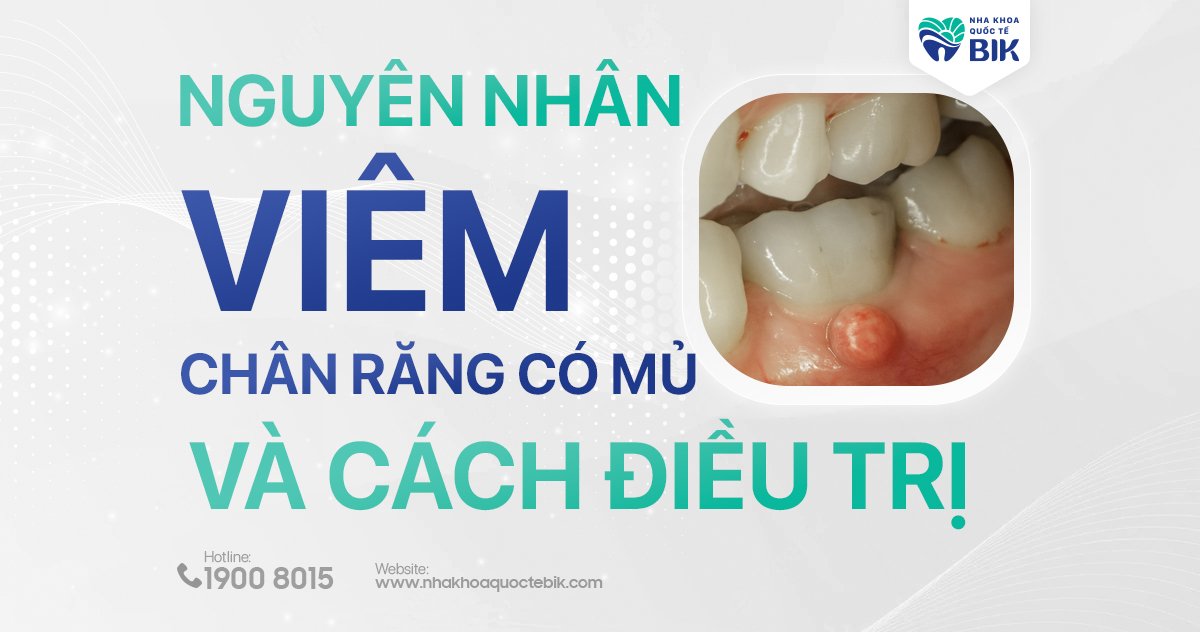
What is purulent periodontitis?
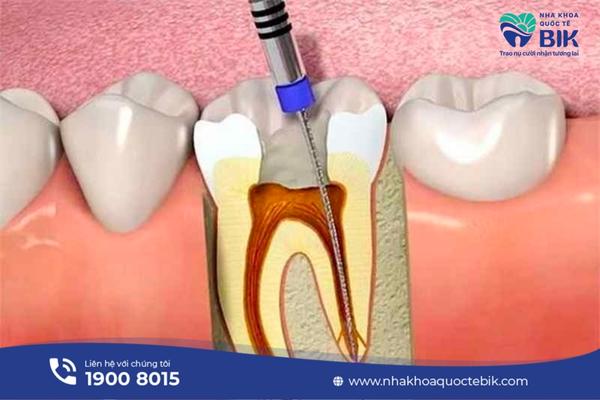
Human teeth consist of enamel, dentin, and pulp. Enamel is the hardest outer layer, protecting the other parts of the tooth. Inside is the dentin and pulp, which have blood vessels and nerves to connect to the body’s nervous system through the hole at the top of the root.
The root is the root of the tooth in the alveolar bone, surrounded by the gums. Purulent periodontitis is an infection in the pulp or gums, creating an abscess around the root. This condition is very dangerous to health, and needs to be cared for and treated promptly and properly to avoid dangerous consequences.
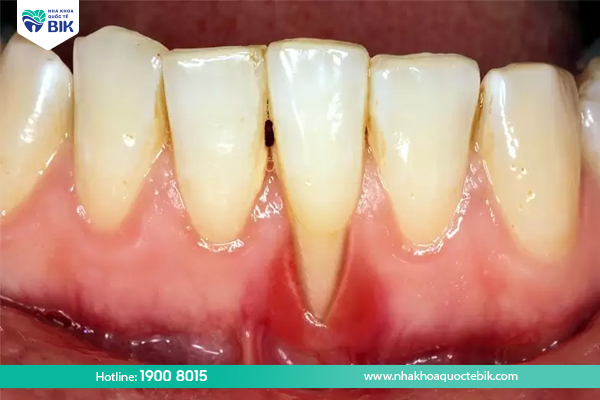
Causes of purulent periodontitis
Pure periodontitis is an infection of the gums, caused by two main causes: gingivitis and pulpitis.
Periodontitis
Causes of gingivitis include failure to maintain proper oral hygiene, food stuck between teeth that is not cleaned, and failure to have regular dental cleanings. In addition, brushing too hard or flossing with a toothpick can damage the gums, leading to gingivitis with symptoms such as bad breath, bleeding gums, swelling, redness, and loose teeth.
If not treated promptly, gingivitis will develop into periodontitis, which can spread to infection, bacteria will thrive due to food stuck between teeth. At that time, the gums will abscess, form pus, the bone will be lost and the gums will recede, causing loose teeth. Gingivitis can also become more severe and develop into periodontitis.
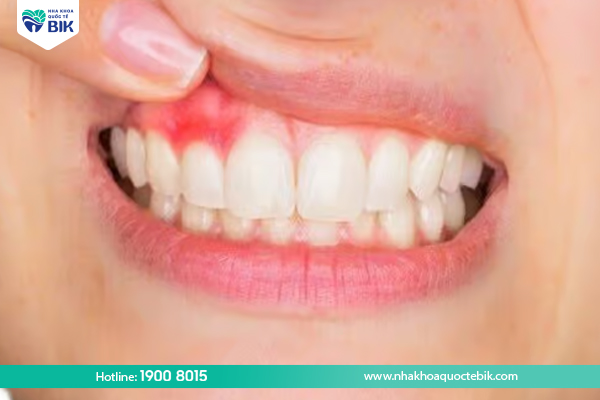
If not treated promptly, gingivitis can lead to purulent periodontitis, which seriously affects oral health. Treatment must be done immediately and properly, otherwise it can cause pain and discomfort for the patient, even leading to tooth loss and affecting life.
Pulp Disease
The pulp is affected by infection spreading from other parts of the tooth. When the tooth is decayed, bacteria will destroy the enamel and dentin to penetrate the pulp. Or prolonged periodontitis can spread to the pulp.
If not treated promptly, pulpitis will form an abscess at the root and root of the tooth, causing pain and bad odor. If left untreated, the pulp can become seriously infected, leading to purulent periodontitis and tooth loss. If the pus spreads into the bloodstream, it can cause a life-threatening infection.
Some other causes
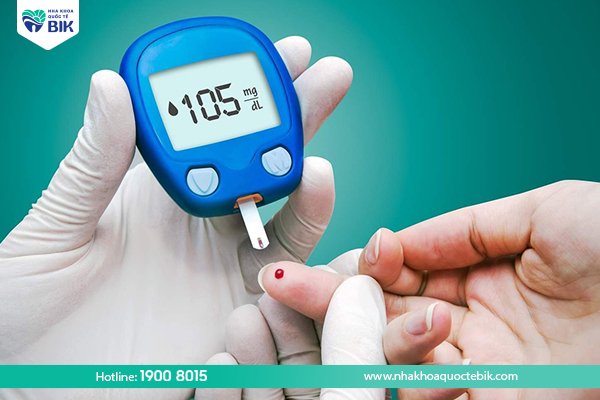
In addition to the two common reasons mentioned, some other causes can also cause purulent periodontitis, including:
- Damage to the bite of the tooth
- Diabetes.
- Use of certain medications.
- Weakened immune system.
- Endocrine disorders,…
Signs of purulent periodontitis
Signs of purulent periodontitis are easy to recognize, patients can recognize through Pain symptoms and external signs:
-
- Pain in the teeth, spreading to the jaw, ears and neck. Pain increases when chewing and cannot chew the painful part.
- Teeth hurts rise, wobble and change color.
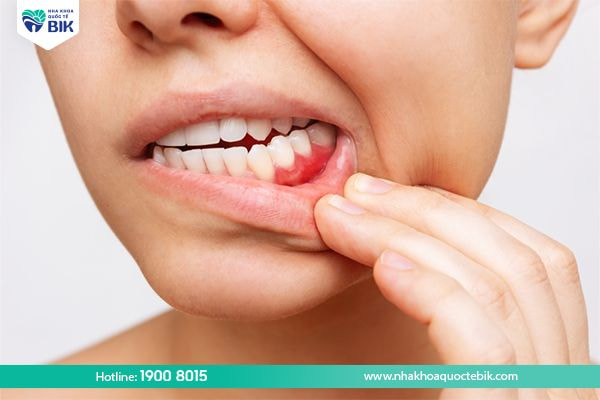
- Gingiva is swollen, painful and soft when pressed, bleeds easily, and sometimes pus oozes out when pressed.
- The facial area near the tooth hurts swollen, hot and red.
- Nodes appear in the neck, under the jaw, painful to the touch, foul-smelling mouth, and fever.
- A pus mass appears in the area tooth root, when the pus bursts can reduce pain.
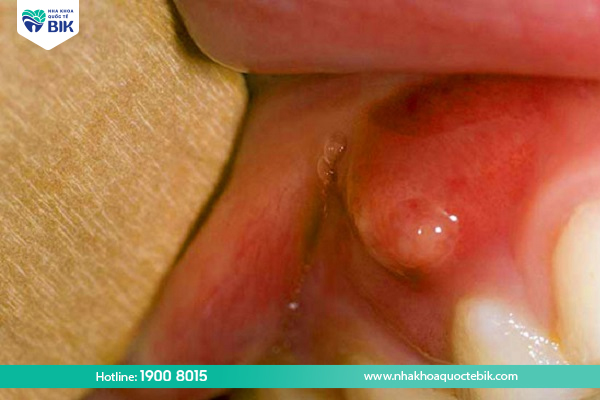
How to treat pus in the tooth root
When treating pus in the tooth root, the dentist will clean the infected area and relieve the pain. Depending on your symptoms, the dentist may order an X-ray to determine the location and assess the surrounding areas for infection so that timely intervention can be made.
Methods of treating pus in the tooth root:
Draining the pus
The dentist will make a small cut at the infected tooth root to drain the pus. They will then clean the infected area to prevent the infection from spreading.
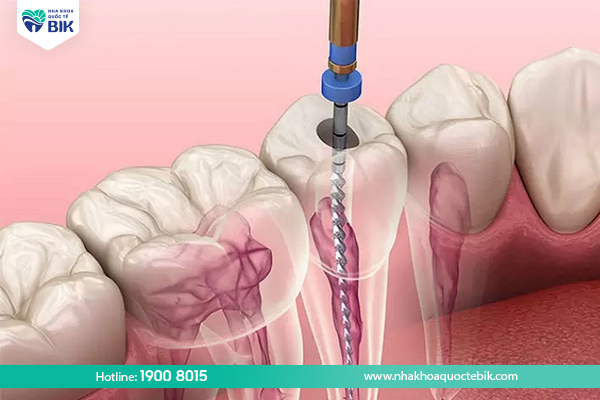
Pulpectomy
The pulp is the soft inner part of the tooth that contains nerves, connective tissue, and blood vessels. A root canal is usually performed to protect a tooth with cavities or pus in the tooth by drilling a small hole in the tooth and removing the pulp. After the root canal, the inside of the tooth will be thoroughly cleaned before being filled or crowned with porcelain.
Tooth extraction
If the inflammation is severe enough to damage the tooth, the dentist may decide to extract the tooth before cleaning the infected area.
Antibiotics
If the infection in the gums has spread or your immune system is not strong enough to fight it, the dentist will prescribe antibiotics to treat it.
Minor surgery to remove foreign objects
If your periodontitis is caused by a foreign object such as a fish bone or toothbrush bristle, the dentist will have to perform a minor surgery to remove it. They will then clean the infected area.
Preventing purulent periodontitis from recurring after treatment
After treatment, you need to pay attention to the following to prevent purulent periodontitis from recurring:
Take care of your teeth every day by brushing your teeth after every meal and before going to bed. At the same time, use dental floss to remove food particles stuck on your teeth.
Rinse your mouth with warm salt water during the day to effectively kill bacteria.
Regular dental check-ups and cleanings depend on the condition of each person’s tooth enamel.

What medicine should you take for periodontal abscess?
There are a few medicines you can take when you have periodontal abscess, but be sure to see a doctor and follow his or her instructions for safer use.
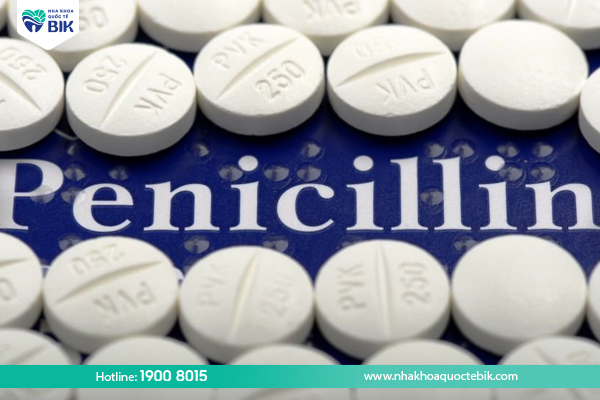
Antibiotics
The function of antibiotics is to kill and prevent the growth of bacteria that cause periodontitis. In particular, P. Gingivalis bacteria in the oral cavity are associated with periodontitis.
Penicillin: Used for moderate to severe cases of periodontitis. The dosage is 500 milligrams (mg) every 8 hours or 1,000 milligrams (mg) every 12 hours.
Erythromycin: Has the same effect as Penicillin and is used for patients who are allergic to Penicillin.
Clindamycin: Clindamycin is effective against many different types of bacteria, including bacteria in the oral cavity. The specific dosage will be prescribed by the doctor depending on the condition, usually 300 mg or 600 mg every 8 hours.
Azithromycin: In case the patient is intolerant to Penicillin, the doctor may prescribe Azithromycin instead.
Tetracycline: Tetracycline is an antibiotic that helps prevent gum ulcers, reduces bleeding gums and effectively relieves pain, in addition to inhibiting bacteria.
Painkillers
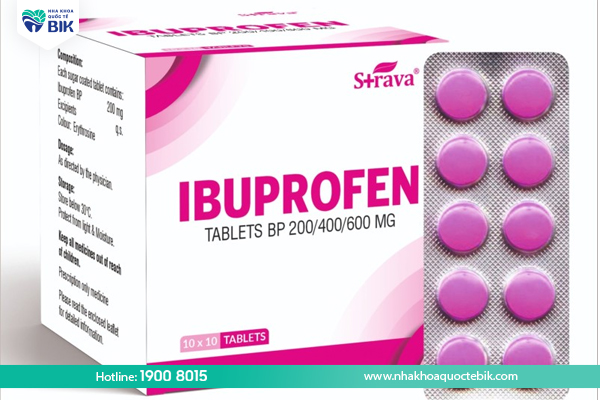
One of the ways to treat purulent periodontitis is to use painkillers. Pain is an uncomfortable symptom that patients with periodontitis have to endure, making it difficult to eat, drink and clean their teeth. Therefore, doctors often prescribe painkillers to help patients feel more comfortable.
Acetaminophen: There are many forms of Acetaminophen with different concentrations, helping to relieve pain quickly. This drug is suitable for many people and has few side effects. However, pregnant women or people with sensitive bodies may experience nausea after use.
Ibuprofen: Ibuprofen is a painkiller used for many different types of pain, including pain caused by gingivitis. Ibuprofen comes in many forms such as tablets, capsules, and syrup. Although considered safe, patients with kidney failure, asthma or stomach ulcers should be careful when using it.
Local anesthetics
Anesthetics such as Lidocaine and Prilocaine work to numb the skin or mucous membranes. Under the influence of this drug, the patient will not feel pain in the damaged gum area.
Remember not to use anesthetics on your own to avoid unwanted side effects. Some common side effects include: numb gums, nausea, swollen gums, etc.
Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs
Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs help control and prevent the spread of ulcers. In addition, they also reduce symptoms of swelling and pain, helping patients feel more comfortable. However, caution should be exercised when using them for people with a history of peptic ulcers.
Corticosteroids
Corticosteroids are also an option for treating purulent periodontitis by using which type of drug? Corticosteroids contain active ingredients that help fight inflammation, fight bacteria and relieve pain. Therefore, this medicine helps eliminate harmful bacteria in the mouth and significantly improves the condition. Using this medicine helps support the treatment of purulent periodontitis effectively. Patients need to follow the dosage prescribed by the doctor, do not increase or decrease the dosage on their own.
Effective prevention of purulent periodontitis
To protect your teeth, make sure to brush your teeth thoroughly twice a day, use dental floss instead of bamboo toothpicks to remove excess food. Rinse your mouth with salt water to kill bacteria and have regular dental check-ups every 6 months to detect oral health problems early.
Maintain a healthy diet for oral health, limit foods rich in sugar and acid, as well as hot or cold spicy foods. Supplement calcium and vitamins from nutritional sources such as eggs, milk, beans, mushrooms, …
Here is complete information about purulent periodontitis, including causes, symptoms and treatments. If you find yourself suffering from this condition, contact a reputable dental clinic for timely advice and treatment.