Gingival not attached to the tooth root is a fairly common condition and is mainly caused by bacterial attacks that damage and weaken the gums over time. If not treated promptly, this condition will worsen and cause more serious complications and even tooth loss.
1. What is gingival not attached to the tooth root?
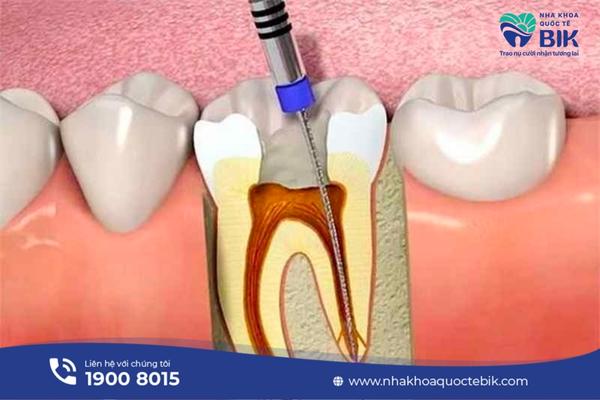
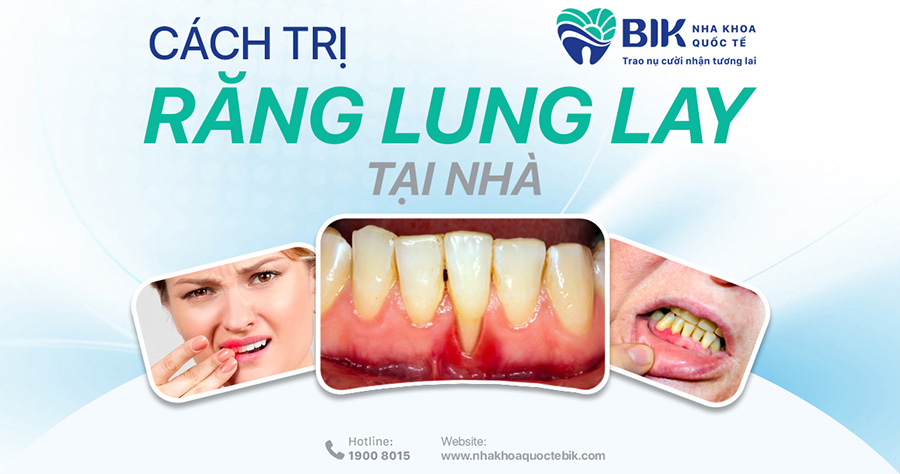
Gingival not attached to the tooth root is a fairly common condition today in which the gum tissue will separate from the tooth root, creating gaps. This condition is easily visible to the naked eye, the exposed gum makes the tooth longer than usual and the dentin will also be exposed.
Healthy gums are usually light pink and adhere tightly, supporting the tooth to stand firmly on the jaw, so if the gums are separated, this is a sign of serious oral problems. From there, eating and daily oral hygiene also become more difficult.
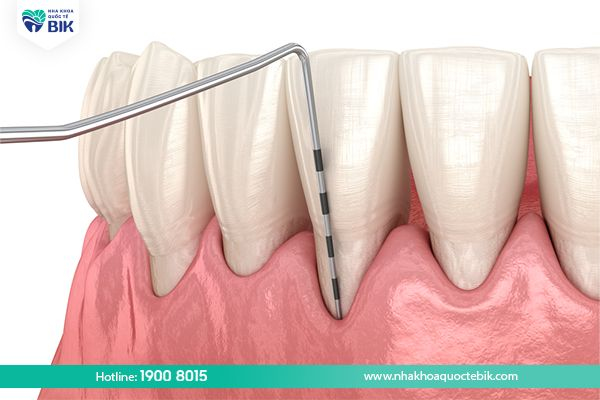
2. Causes of gums separating from teeth
Gingiva separating from teeth can be due to the following reasons:
2.1. Improper oral hygiene
Improper oral hygiene is the main cause of oral diseases leading to the condition of gums not firmly attached to the tooth roots. When food plaque is not cleaned for a long time, it will calcify in the oral cavity and form tartar.
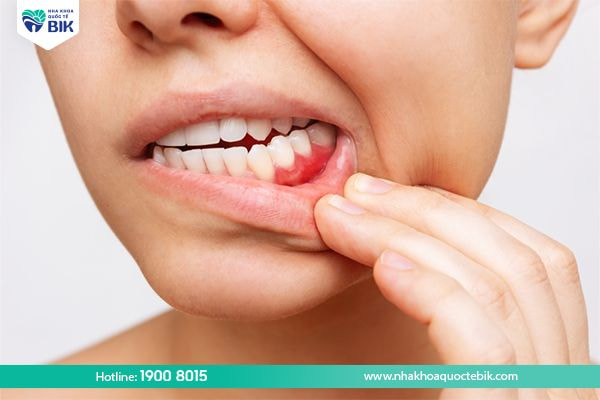
This dental plaque often exists between the tooth root and the gum, which is an ideal living environment for many types of harmful bacteria. Bacteria will then easily multiply and develop, attacking and damaging the gums, leading to gingivitis and gum recession.

2.2. Due to oral diseases
Some oral diseases such as gingivitis, periodontitis, periodontitis, etc. are also the cause of the gums not being firmly attached to the teeth. Basically, when suffering from these diseases, the gums are already infected and damaged, so if not treated promptly, they will progress more severely, causing the gums to gradually weaken and then no longer be able to adhere firmly to the teeth.
2.3. Due to lack of nutrients
The body’s deficiency of certain vitamins such as vitamin E, vitamin C, iron, zinc, etc. will also cause the gums to become weaker. At that time, the gums cannot adhere firmly to the tooth body, causing exposed gums.

2.4. Congenital
Research shows that families with a history of dental problems will have a higher risk of oral diseases if they do not take proper care of their teeth. In particular, gums separating from the teeth can also be hereditary from parents to children.
3. How does gum not attach to the tooth root affect?
The gum not attaching firmly to the tooth will create a gap, but if this condition has just occurred in the early stages, it will not cause too much dangerous effects on oral health. If it is not treated and left for a long time, it will be quite dangerous.
The exposed gum position will be a gathering place for many harmful bacteria, so they will have favorable conditions to accumulate and multiply more and more, thereby increasing the risk of oral diseases. When this condition becomes more severe, the patient may experience blood infection, a high risk of tooth loss, and overall health is negatively affected.

4. Overcoming the condition of the gums not firmly attached to the tooth root
To overcome the condition of the gums not firmly attached to the tooth root, you can apply the following methods:
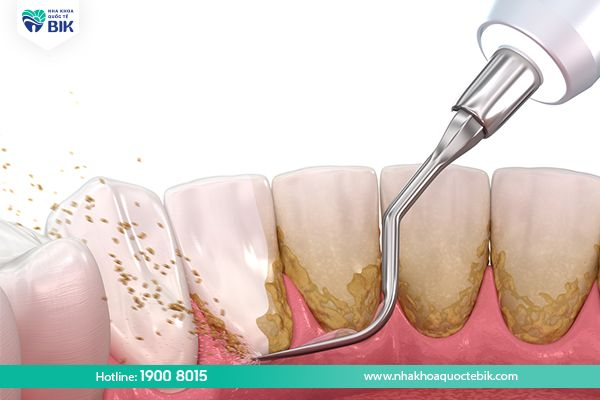
4.1. Scaling
In cases where the gums do not adhere tightly to the tooth root due to thick tartar buildup, scaling is the best method. After the hard plaque layer is removed, harmful bacteria will also be destroyed, effectively overcoming the condition of gums not adhering firmly to the tooth root.
4.2. Vitamin Supplements
If the gums are separated from the tooth roots due to a lack of necessary nutrients, you should pay attention to supplementing all the necessary nutrients through foods such as meat, fruits, green vegetables, etc. Once health is guaranteed, the body will be able to fight against bacteria that are harmful to the gums and teeth.

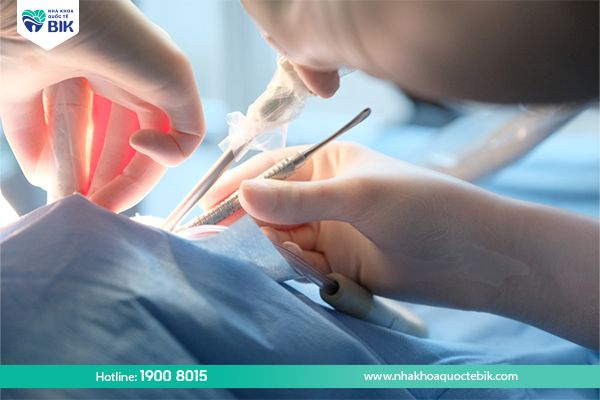
4.3. Surgery
If the gums are separated from the gums but are not treated early, the doctor will be forced to prescribe surgery when the condition becomes more severe. At this time, after examination, the doctor will prescribe gum grafting or gum flap suturing to fix the condition of the gums not firmly attached to the tooth body.
5. Preventing gums from separating from teeth
To prevent gums from separating from teeth, you should note the following:
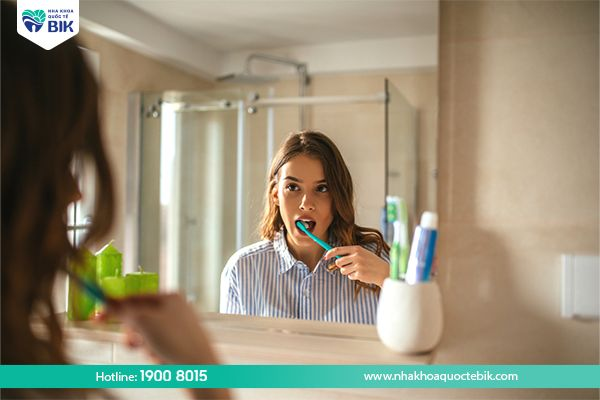
5.1. Proper oral hygiene
Brush your teeth with a soft-bristled toothbrush at least twice a day, especially after eating to ensure that food debris on the tooth surface is removed.
– Pay attention to using just enough force to brush your teeth in a circular motion to avoid affecting the gums.
– Use a toothpaste that nourishes the gums to make them healthier.
– Replace your toothbrush every 3-4 months to ensure that bacteria do not accumulate and attack the teeth and gums.
– Use dental floss to completely remove food debris between teeth.

5.2. Scientific diet
To prevent the gums from not firmly adhering to the tooth roots, you should also follow a scientific diet. Limit spicy foods, carbonated soft drinks, foods that are too hard or too chewy,… to avoid damaging the gums. In addition, do not smoke to avoid more serious damage to the gums.
5.3. Regular check-ups
Go to the dentist for regular check-ups and scaling at least twice a year as advised by your dentist so that bacteria do not have a chance to develop and attack your gums and teeth. In addition, this also gives your dentist the opportunity to check and promptly treat any oral diseases if any.
There are many causes of gums not being firmly attached to the teeth, the main cause of which is improper oral hygiene. To effectively overcome this condition, patients should go to a reputable dental facility for examination, find the cause and implement thorough treatment measures.