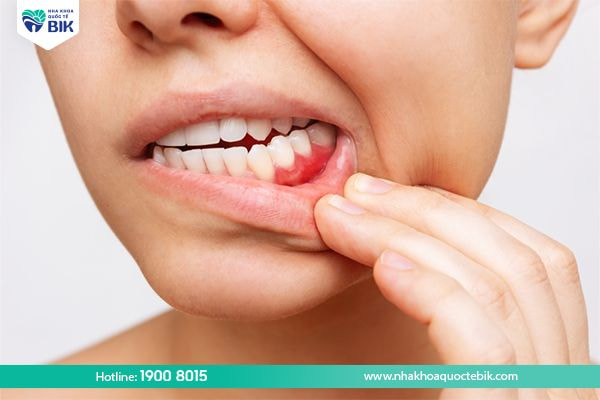
The phenomenon of bleeding gums when brushing teeth or flossing with relatively strong force is completely normal. However, if the gums bleed without any impact, it can be a sign of quite common oral diseases. In cases where the body has some other serious diseases, it can also cause the gums to bleed continuously and for a long time.
1. Why do gums bleed?

Want to know what gum bleeding is? First we need to find out Why do gums bleed?
Gum bleeding is a condition of bleeding in the gums and gums and is accompanied by some symptoms such as bad breath, swollen gums, … Gum bleeding is a symptom of some oral diseases, or it can also be a sign of more serious health problems.
2. What oral diseases cause gum bleeding?
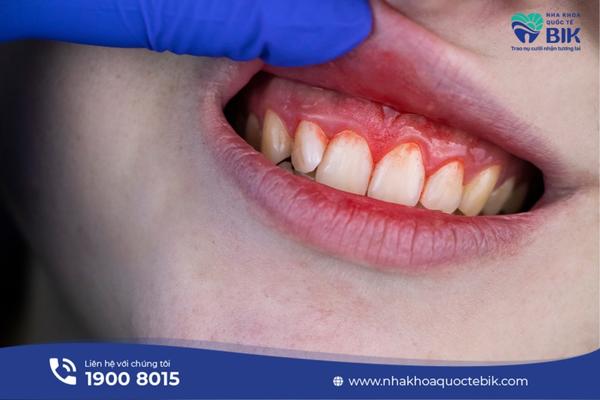
2.1. Gingivitis with bleeding gums
Patients with gingivitis (gingivitis) are due to poor oral hygiene, not using dental floss to completely remove plaque between teeth, and remaining food will irritate the gums and cause bleeding. In addition, tartar on the tooth surface and tooth roots will also cause bleeding gums. The more severe the gingivitis, the more bleeding.
2.2. Periodontal disease with bleeding gums
Bleeding gums can also be caused by periodontitis. If not treated promptly, gingivitis will lead to periodontitis. At this time, the gums can become severely inflamed, infected, and cause the tooth roots to be exposed. This condition, if prolonged, will damage the bone tissue that supports the teeth and cause tooth loss.
2.3. Dental abscess
A dental abscess is a collection of infected pus in the tooth root area. A dental abscess can lead to bleeding gums, causing pain and high fever.
3. Systemic diseases that cause bleeding gums

3.1. Hormonal changes in women
During periods such as puberty, pregnancy or menopause, hormones in a woman’s body will change. This phenomenon will increase the risk of bleeding gums.
3.2. Vitamin deficiency
Bleeding gums are also a sign that the body is deficient in vitamin C or vitamin K. These vitamins help strengthen bones, teeth and help blood clot properly. Therefore, they play a very important role in preventing dental problems.
3.3. Liver disease
The liver is an important organ of the body that performs many functions, including blood clotting. Therefore, any liver disease can affect liver metabolism and eventually lead to many consequences, including bleeding gums.
3.4. Diabetes

The oral cavity of diabetic patients often does not have the ability to fight harmful bacteria. Therefore, patients are very susceptible to gum infections, diseases related to the mouth, especially bleeding gums. In addition, high blood sugar levels make bleeding gums more difficult to heal.
3.5. Leukemia
Leukemia is a type of blood cancer caused by an increase in the number of white blood cells in the body. The body will have symptoms such as: excessive fatigue, fever, vomiting, easy bruising, bleeding, etc. Platelets in the blood are responsible for helping the body stop bleeding. People with leukemia have very few platelets in their blood, making it difficult to stop bleeding in some parts, including the gums and teeth.
3.6. Thrombocytopenia
Thrombocytopenia is a condition in which the body does not produce enough platelets to help blood clot. This leads to bleeding at various levels, so if you experience bleeding gums that cannot be stopped, it may be a sign of thrombocytopenia.
3.7. Hemophilia
Hemophilia is a genetic disorder that leads to abnormal bleeding. In severe cases, medication or clotting factors may be required to prevent unwanted risks.
3.8. Scurvy
Scurvy is a disease caused by a deficiency of vitamin C, which can lead to physical weakness or spontaneous bleeding, including bleeding in the gums. Scurvy can be treated by adequate vitamin C supplementation.
4. Treat bleeding gums at home?

If bleeding gums are just due to daily habits, you can apply the following methods to effectively treat bleeding gums at home:
4.1. Proper oral hygiene
Poor oral hygiene will also leave plaque along the gum line, bacteria from plaque can easily attack the gums and tooth roots, causing inflammation leading to bleeding gums. Therefore, you should brush your teeth and floss at least twice a day to prevent bacteria from spreading. Be careful to use a soft toothbrush and not brush too hard to damage your gums, leading to bleeding.
4.2. Supplement nutrition
You should supplement the necessary vitamins for your body from your diet. You should supplement vitamin C to strengthen the immune system and help fight gum infections. Vitamin C is often found in fruits such as oranges, lemons, grapefruits, etc. In addition, vitamin K found in bananas or radishes also helps limit bleeding gums. If you lack these two vitamins, the bleeding will become more severe.
4.3. Quit smoking
In fact, smoking not only increases the risk of lung cancer, heart disease, and stroke, but is also the main cause of periodontitis, which increases the risk of bleeding gums. Quitting smoking will increase the body’s immunity against bacteria, support gum healing, and prevent bleeding.
4.4. Cold compress
With this method, the patient can apply a cold towel or ice wrapped in a thin cloth to the swollen area to limit bleeding and stop bleeding. However, cold compresses are only effective when the gums are bleeding due to trauma or damage to the gum tissue and not due to other diseases.
4.5. Rinse your mouth with salt water
Dilute half a teaspoon of salt and rinse your mouth for a few seconds about 3-4 times a day to reduce bacteria that cause bleeding gums and stop bleeding.
4.6. Drink green tea
Green tea contains natural antioxidants that can reduce the body’s inflammatory response to bacteria in the oral cavity. Drinking green tea every day can prevent periodontal disease and reduce bleeding gums.
4.7. Keep your mind relaxed
Gingivitis and some other oral diseases can be caused by prolonged stress. Negative emotions can directly affect the immune system and cause bleeding gums. Therefore, try to think optimistically and positively to help improve the condition of bleeding gums.
4.8. Medicine for gingivitis and bleeding gums
In cases where the teeth have been scaled and the gums have been restored but the bleeding continues, the doctor will prescribe medicine to treat gingivitis and bleeding gums. Do not use drugs without a doctor’s prescription to ensure oral health safety.
There are many different causes, including serious illnesses of the body that cause bleeding gums. Bleeding gums can still be improved with some simple ways at home. However, if after a few days the bleeding gums still do not stop, you should see a dentist for advice and effective, safe treatment.