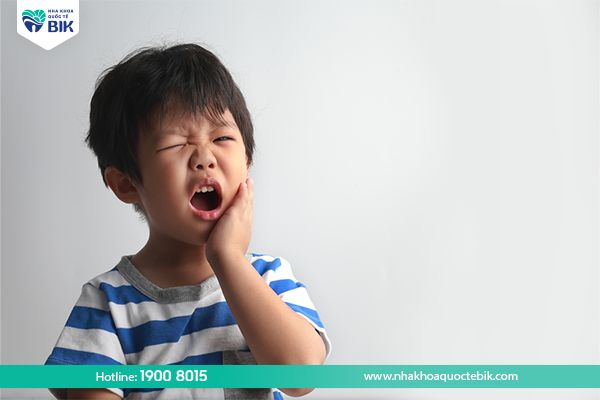
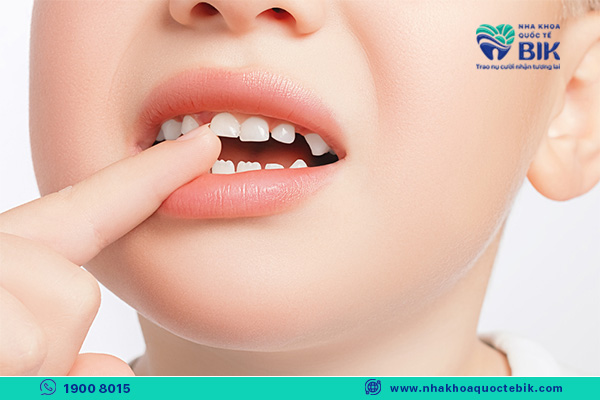
Tooth decay is a common problem in children, especially in the age group of 1 to 3 years old. This condition can cause many consequences such as tooth destruction, damage, loss of aesthetics and affecting the child’s ability to speak. Therefore, parents need to know how to prevent and treat their children when they have early tooth decay.
The structure of the tooth includes a hard outer shell, followed by enamel and dentin. However, the enamel and dentin in children are quite thin, low in calcium and vulnerable. When the enamel is damaged, the child’s teeth will gradually erode and disappear, leading to the size of the teeth becoming smaller. This phenomenon is called tooth decay.
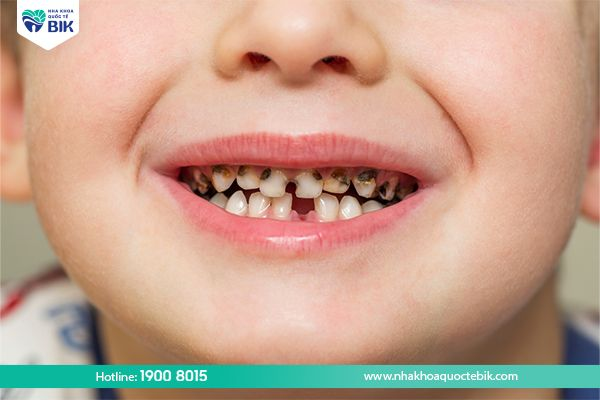
Age of children susceptible to early tooth decay
Tooth decay often occurs in children from 1 to 3 years old, does not cause pain to the child and the decay is usually not as deep as a cavity, but has a large area, is black or brown and has a soft bottom during development. Tooth decay can spread quickly to other teeth if not detected early and controlled promptly. In the end, the child’s teeth will only have small pieces of teeth near the gums, the roots close to the gums, affecting the child’s chewing and communication functions.

The effects of tooth decay in children
Effects on eating and digestion
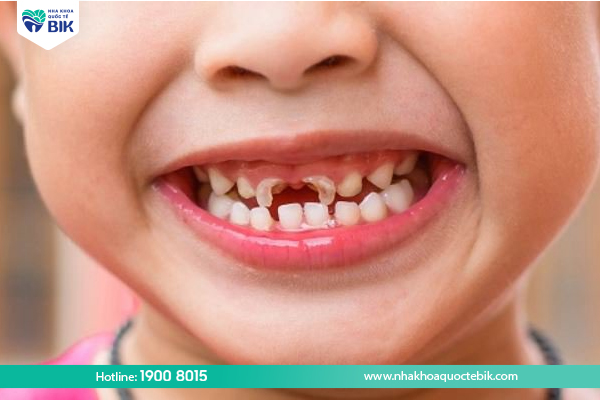
Children usually start to lose their first baby tooth when they are around 5 – 6 years old and their last baby tooth when they are 12 – 13 years old. Usually, every time a baby tooth falls out, a permanent tooth will grow to replace it within 6 to 12 months. However, if your baby’s baby teeth fall out earlier than the above time, after losing a tooth, for a period of time your baby will not have a replacement tooth, which can affect your baby’s eating, digestion and pronunciation.
Affects adjacent teeth
Not only that, when baby teeth fall out, they will carry harmful bacteria, not only affecting that tooth but also causing negative effects on permanent teeth and gums. At the same time, when baby teeth gradually wear down, the pulp will be exposed, dentin will appear, making your baby feel uncomfortable and painful when eating and drinking, easily fussy and anorexic, which can directly affect your baby’s future development.
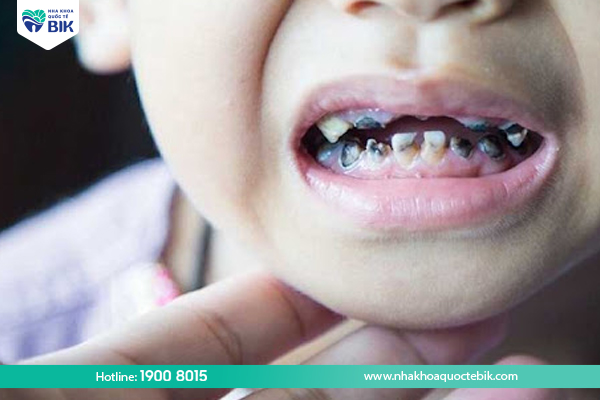
Impact on pronunciation and aesthetics
In addition, when a child’s teeth are worn down due to early loss, especially the front teeth, in addition to causing loss of aesthetics, it can also cause the child to lisp. In fact, it has been shown that many children with severe tooth loss will have difficulty pronouncing correctly, often lisping more than children with healthy teeth. This can make the child feel self-conscious and afraid to communicate with people around them.
Affects the teething process
In particular, tooth decay can also affect the child’s normal teething process, causing permanent teeth to grow abnormally in the future. The reason is that when teeth are decayed or damaged early, the gums will quickly close before the permanent teeth grow in that position. At that time, the permanent teeth will encounter many difficulties and may grow crookedly, causing damage and pain to the child.
Causes of tooth decay in children
Tooth decay in children has many causes, including:
- Bad eating habits, such as eating too many sweets, fast food, dried foods with high sugar content and carbonated drinks, colored drinks, drinking milk at night without cleaning teeth before going to bed.
- Lack of calcium and premature birth can lead to enamel hypoplasia, as well as the use of many antibiotics or drinking milk at night with high sugar content and strong adhesion, causing acid to destroy tooth enamel.
- Full-mouth cavities or a diet lacking in calcium and fluoride can also damage the baby’s teeth.
- The use of antibiotics such as Tetracycline, Doxycycline during pregnancy can cause the baby’s teeth to not develop well, the enamel is of poor quality and vulnerable.
- Improper oral care can also create conditions for bacteria to invade tooth enamel and cause tooth decay.
- In addition, jaundice in children can also affect tooth enamel.

What nutrients are lacking in children?
Hypoplastic teeth can occur when the fetus is born prematurely, lacks calcium, uses too many antibiotics or is due to the daily diet (such as drinking milk at night with high sugar content and strong adhesion, causing tooth enamel to be easily destroyed by acid).

How to prevent and treat tooth decay in children?
Proper oral hygiene for children
When the baby’s first tooth appears, that’s when the mother needs to take special care of the baby’s teeth. Initially, parents can clean the baby’s baby teeth by using a soft gauze to wipe every morning and after the baby eats. After the baby finishes eating, give the baby water to wash away the food, clean the teeth and throat, and prevent tooth decay and sore throat for the baby.
When your baby reaches 2 years old, his teeth have developed more completely, he can eat many types of food like adults, so he needs to take better care of his teeth. Parents should use toothpaste containing fluoride to prevent tooth decay when brushing their baby’s teeth. For children who often eat sweets and snacks, parents should brush their teeth right after eating to avoid tooth decay and cavities.
When your baby reaches 3 years old, parents should teach their baby to brush their teeth properly (brush from bottom to top, make sure to brush all 3 surfaces of the teeth: outside – top – inside at least 2 times in the morning when waking up and in the evening before going to bed).
Notes on your child’s diet
During the period when children are changing their baby teeth and growing permanent teeth, parents should add foods rich in calcium and fluoride to their child’s diet such as sea fish, eggs, animal liver, fresh milk, etc. In particular, carrots are also a food that is beneficial for oral health, helping teeth to be strong, heal quickly when damaged and reduce bleeding gums. However, parents should limit their children’s use of foods that are not good for oral health such as carbonated drinks, soft drinks, cold water, candy, etc.

Eliminate bad habits that affect oral health
To protect your child’s teeth, parents should pay attention not to let their child drink from a bottle or hold a bottle while sleeping. At the same time, limit the child’s use of teeth to bite hard objects, do not let the child eat candy, drink carbonated water and eat at night. If the child has a habit of drinking milk at night, parents need to give the child water to clean the mouth after drinking milk. However, most doctors recommend stopping night feeding when the child reaches the age of 8 – 10 months. The reason is that night feeding will interrupt the child’s sleep, affect height development and can cause damage to baby teeth. For children who have a habit of holding rice in their mouth, parents need to check the child’s mouth after eating to avoid excess food sticking to the teeth and causing tooth decay.
Pay attention when giving medicine to your child
Using antibiotics can cause many problems for children’s teeth such as discoloration, enamel damage and difficulty in recovery. Therefore, to protect your baby’s teeth, parents should be careful and not give their children antibiotics without a doctor’s prescription.
Regularly take your baby for regular dental check-ups
To protect your baby’s oral health, parents should take their baby for regular dental check-ups every 3-6 months. In cases where your baby has tooth decay or loose baby teeth early, parents should take their baby to a reputable hospital for a dental specialist to diagnose and provide appropriate measures to prevent crowded or crooked teeth in the future.
Hopefully the above information will help parents better understand the causes of early tooth decay in their baby and how to prevent and treat them for their children. Taking your baby for regular dental check-ups is very important to detect oral diseases early and treat them promptly, avoiding serious conditions in the future.